How to Build a Triangular A-Frame House
I design private houses in the shape of the letter A - like a hut. And I think that there is no more original housing.
Triangular houses were popular abroad in the fifties and seventies, and in Russia they are now in fashion. There is an opinion that A-houses are only suitable as a summer house, but this is not true: many of my friends live in them all year round. Such houses are made using frame technology, which means they are light and warm. Against the background of the typical and boring architecture of the private sector, they look fantastic.
About 200 triangular houses have been built according to my designs. I will tell you about their structure, how much it costs to build and about typical mistakes.
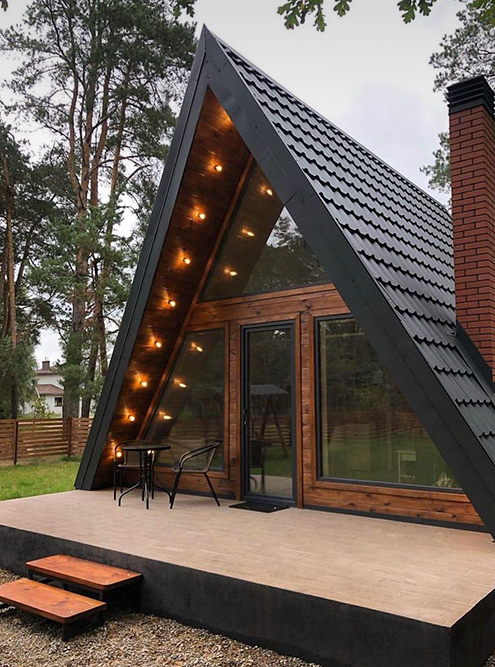
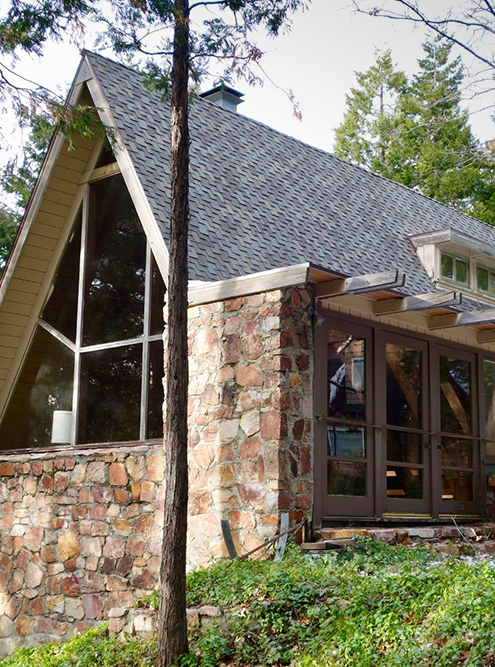


What is A-frame
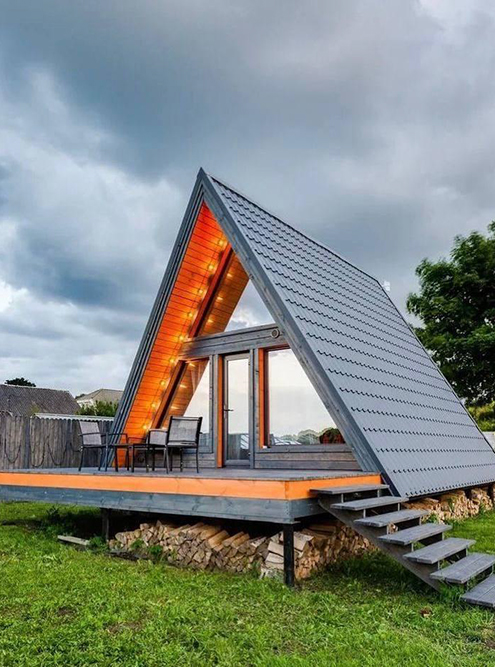
Unlike a regular rectangular house, a tent house does not have two walls - their role is played by a gable roof that stretches from the ridge to the foundation. Sometimes people even say to me: "I see the roof, but where is the house?" In addition, in modern A-houses, the gables are often made with panoramic glazing. It turns out that, strictly speaking, there are no other two walls either.
The classic A-house is 50-60 m² in area and 6-10 meters high . The house has two floors, with the second floor usually used for sleeping, as it is not always possible to stand up to one's full height there. The house is ideal for a family of two or three people. If desired, a more spacious A-house can be built , in which a larger family can live comfortably.
A-shaped houses were built in many countries, but they were most developed in the United States after World War II. Americans regarded them as summer cottages and often built them near bodies of water. The houses were not insulated or connected to central communications in order to make them more affordable.
Then manufacturers began offering ready-made house kits, which were made at the factory and assembled on site in a couple of weekends. As a result, a real boom of A-houses began : they were installed by private individuals, and entire recreation centers were built with them. In the seventies, the fashion for hut-like houses faded away. Many of them have already been lost in the USA, and some are still standing - their owners reconstructed them.


Are A-frame, triangle house and tent house the same thing ?
In Soviet times, triangular houses were built in dacha cooperatives, then they were simply called hut-houses. The word "hut" is usually associated with something not very reliable, but already at that time it meant simply the shape of the hut, and not the features of its construction.
In the USA and Europe, the name A -frame is accepted , that is, a frame house in the shape of the letter A. Such houses can also be called A-houses or triangular houses.
All these names mean the same thing - a triangular shaped house.


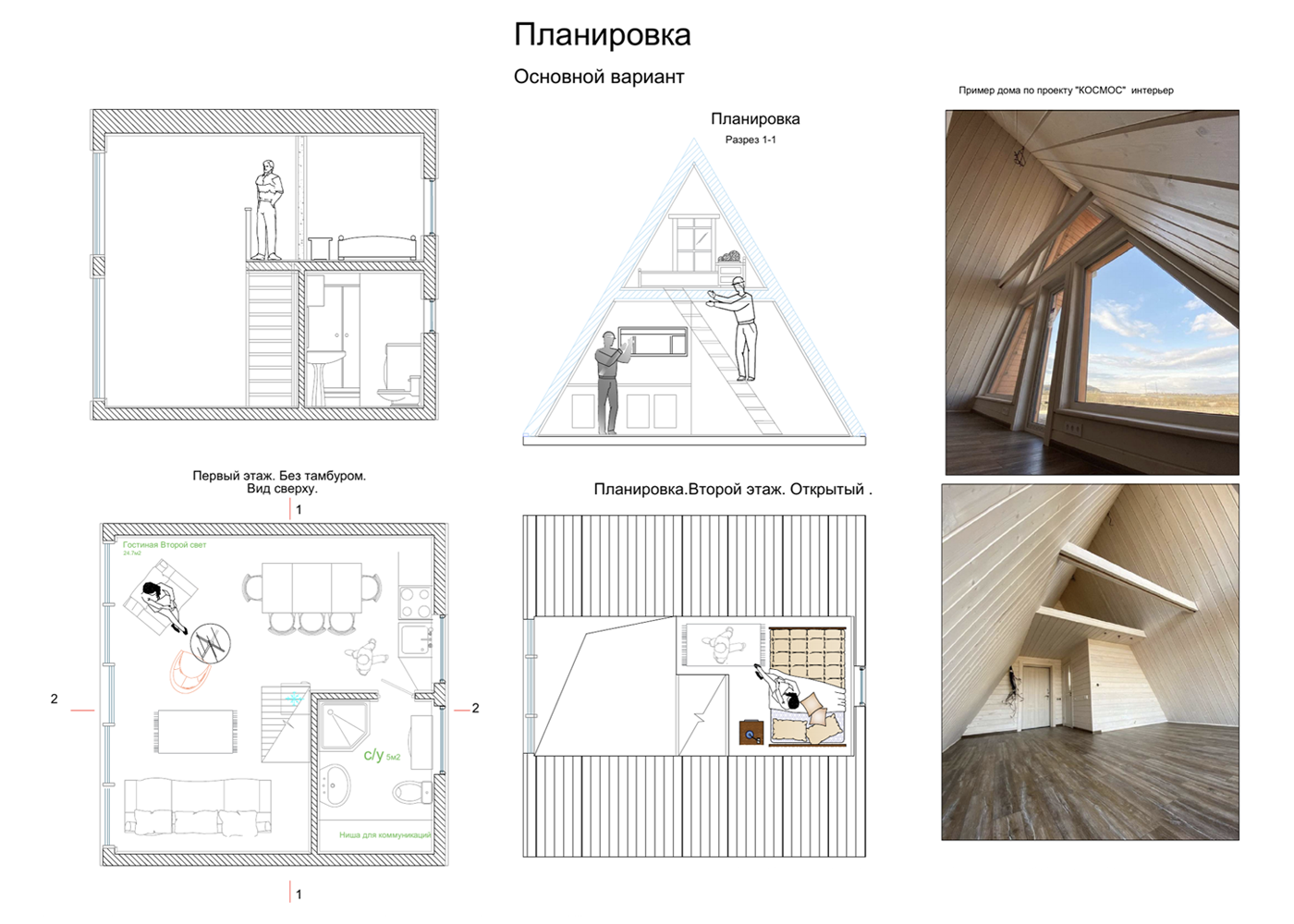
Planning and organizing space in A-frames
The layout of A-houses is determined by their shape.
Corners take up a lot of space. As a rule, the living area of such houses is calculated with a 900 mm indent from the corners. After all, the wall usually goes at a 60° angle, and if you approach it without hitting your head, there will be about a meter left - this distance also depends on the person's height.
Corners are usually used as storage space - you can put drawers there or make a special set.
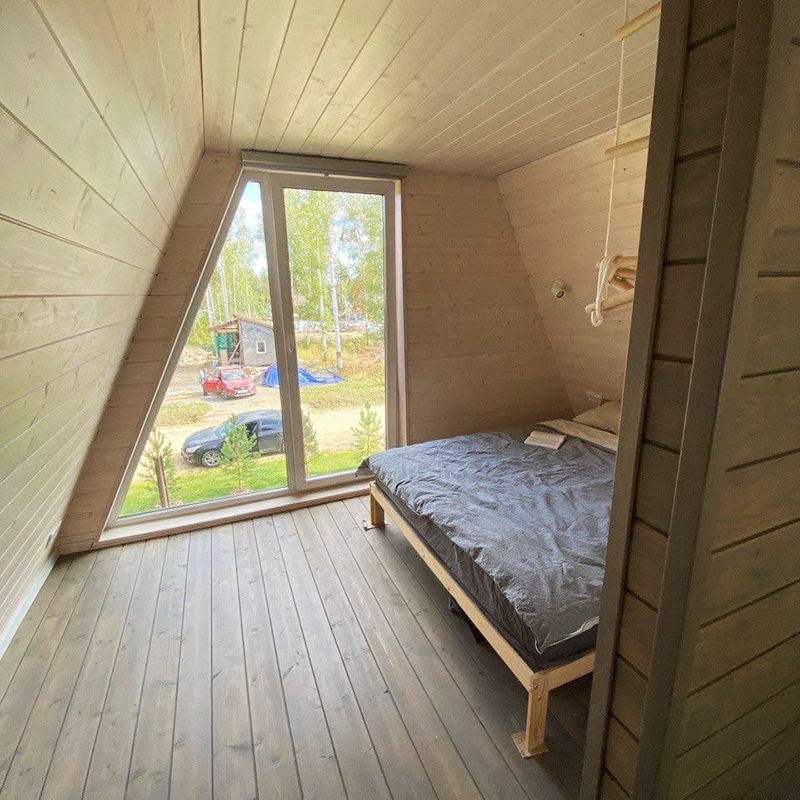
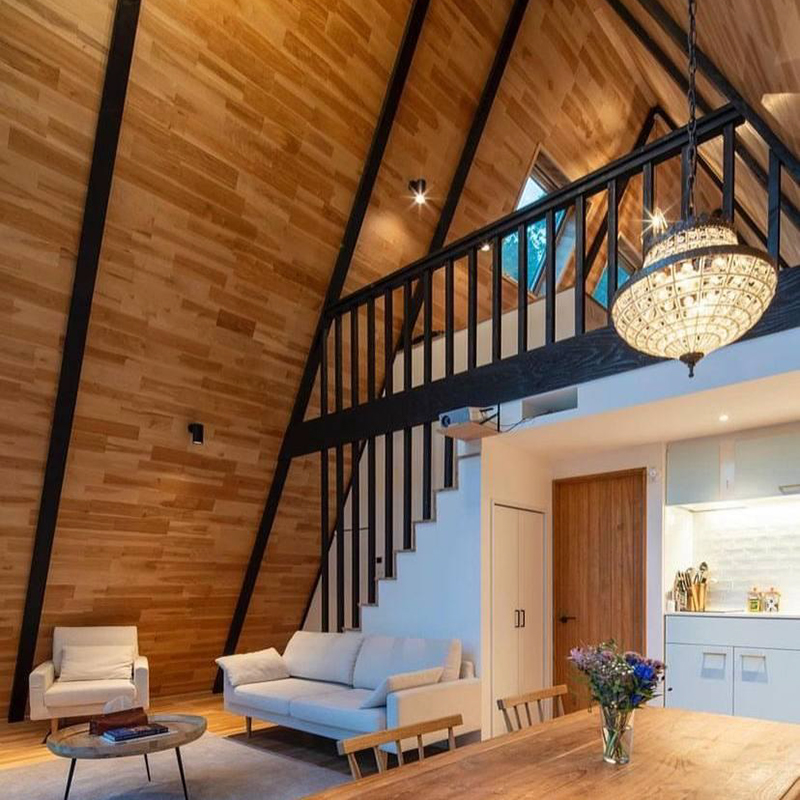
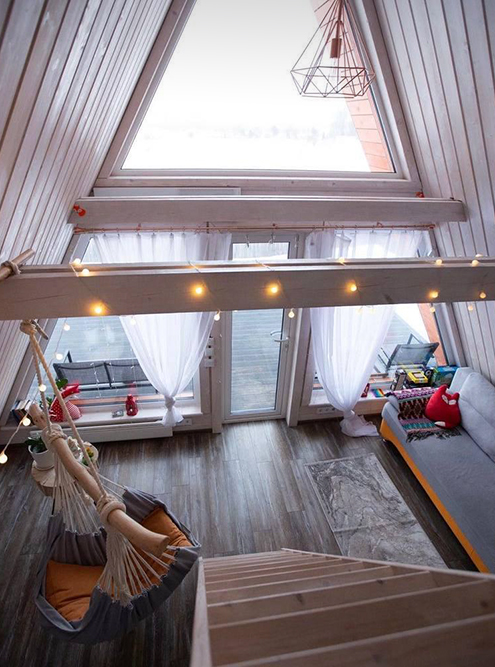
Partially there is no interfloor ceiling. This is also called the second light - the roof of the house acts as a ceiling for the first floor. I think this is a plus, since the light penetrates through large panoramic windows on both floors, and the first floor turns out to be especially bright. Due to the fact that the ceiling in the house is cut off, the area of the second floor is always smaller than the first.
The classic A-frame is two-story. There are many rental houses-huts on the Internet, where the second floor is small, so two people barely fit there. These are small houses of 40 m², which are built for rent. Such houses are in sight, because the owners make advertising campaigns for them.
It seems that an A-house is something small, where you can live for a week at best. In fact, this is not true. There are many large A-houses with a living area of 100 m², where families live permanently. These houses just do not have social media accounts - the owners do not need to show them.
A house with a base of 7.5 x 9 meters will already have a full second floor. Such a house will have two large bedrooms, a bathroom, a kitchen, and a living room. I once even designed a three-story A-house , where the third floor is a small children's room.
In a 6 x 6 meter house with a second light, the second floor will be approximately 4 m² in area, and if the second light is not made and instead a ceiling is built, as in ordinary houses, the second floor will increase in area approximately twice.
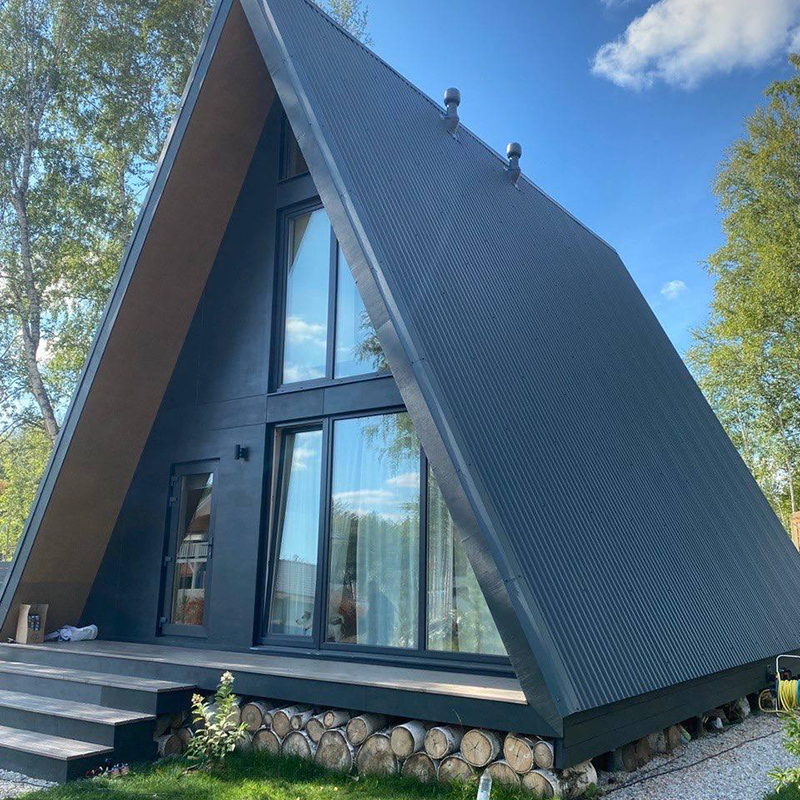
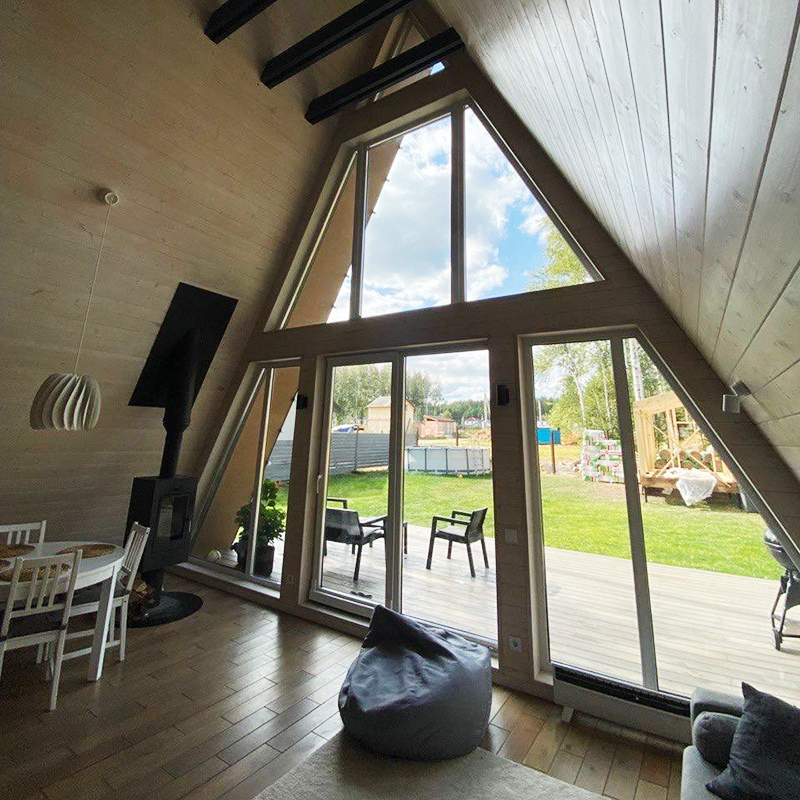



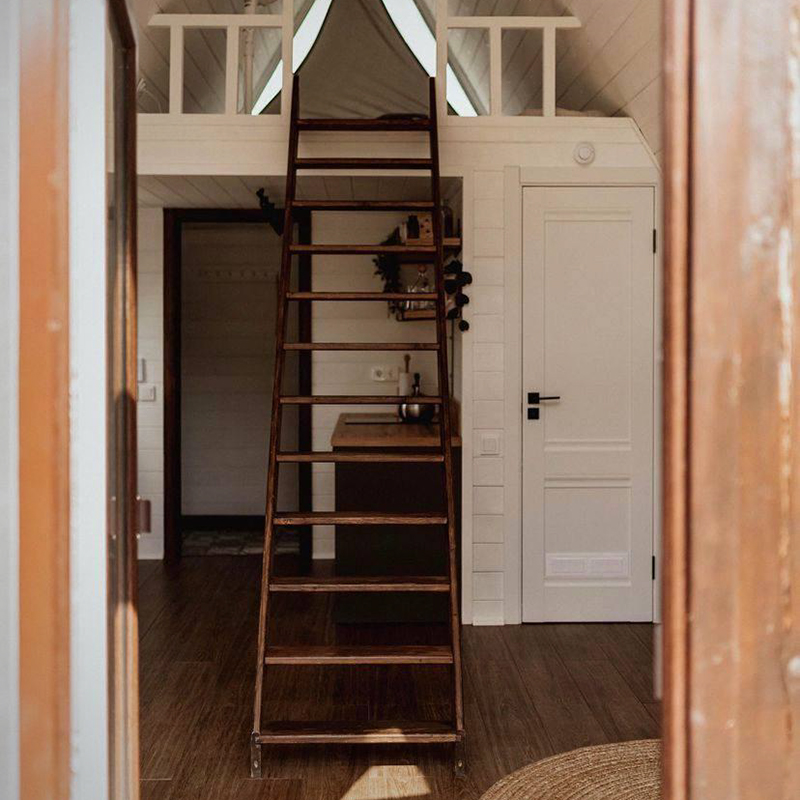
The staircase requires special attention. As a designer, I come across the fact that people try to save on the staircase. It seems that it is a waste of space, and it is also expensive. As a result, we get houses where the staircase is installed at a steep angle. It is dangerous and creates inconvenience when used even by young people.
In a large house, it is certainly easier to make a comfortable staircase than to try to fit it into a 6 x 6 meter A-frame . But if you have to choose between a steep staircase with a clear landing in front of it and a flatter staircase leading to the kitchen, the second option is better
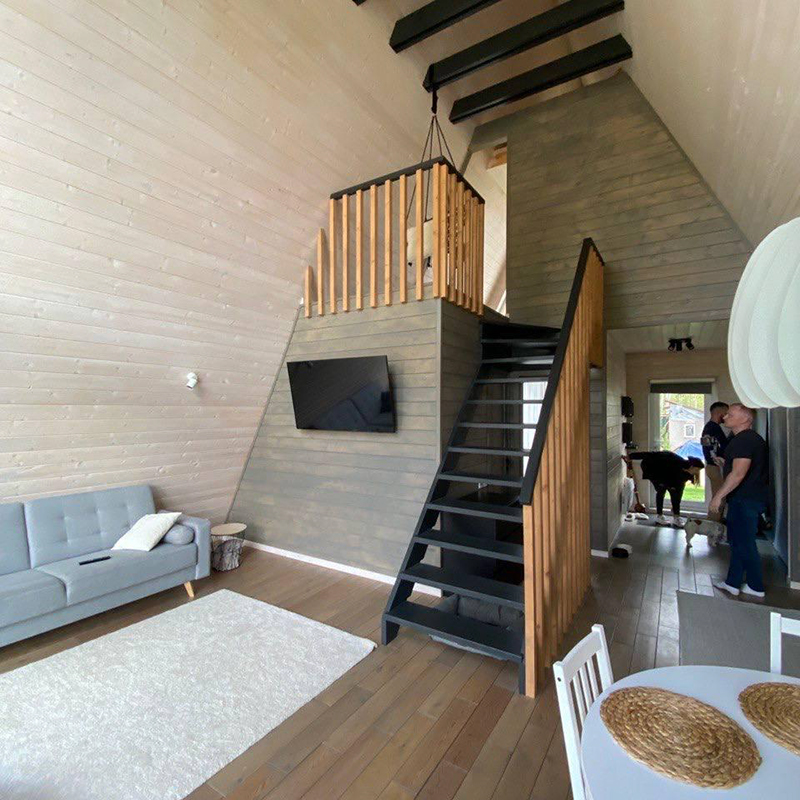
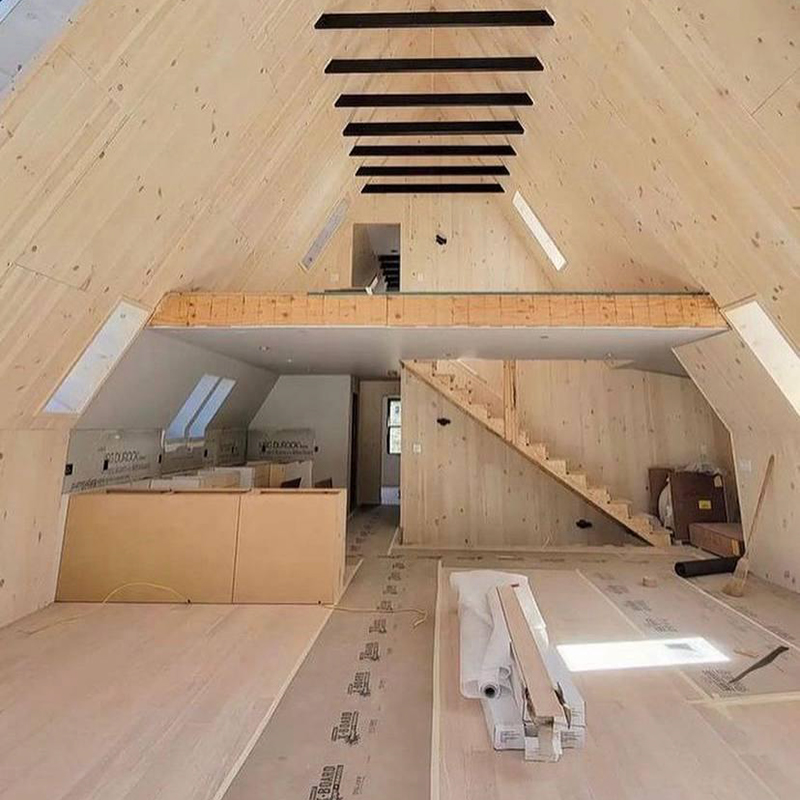




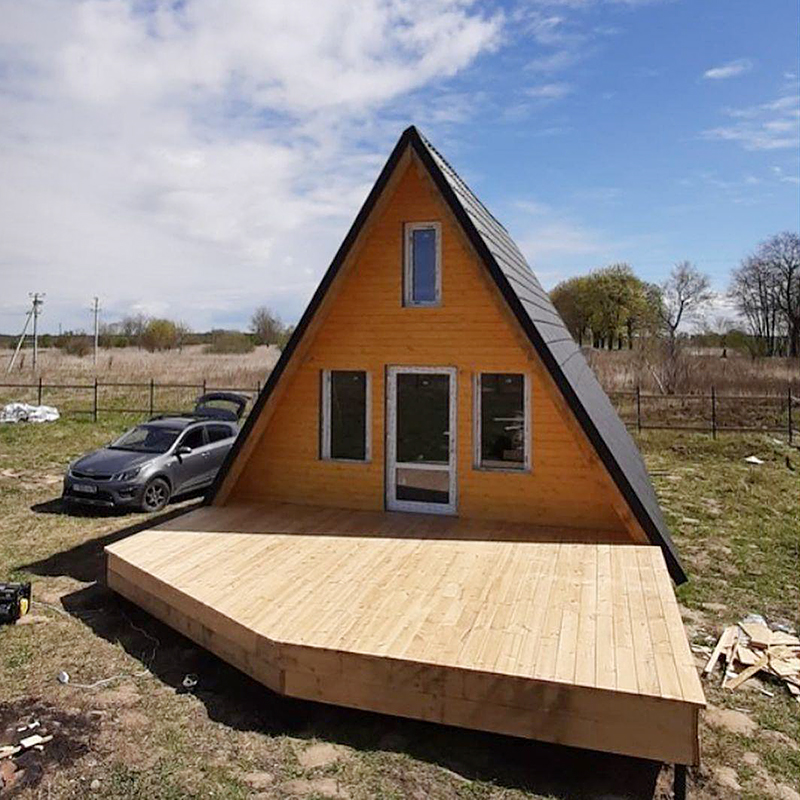
You can make an extension and expand the area. This is usually done when a family has lived in an A-house and the area is not enough. Initially, building an A-frame with an extension is not economically feasible; it is better to increase the A-house itself : for example, build 8 × 10 meters instead of 6 × 6 with an extension. The first option is cheaper and technically simpler.
In addition, I think that A-frames with an extension lose their individuality. It is no longer an A-house , but something incomprehensible. Although I have seen options when it looks more or less beautiful. In my practice, there was only one case when we made an extension in an A-house .
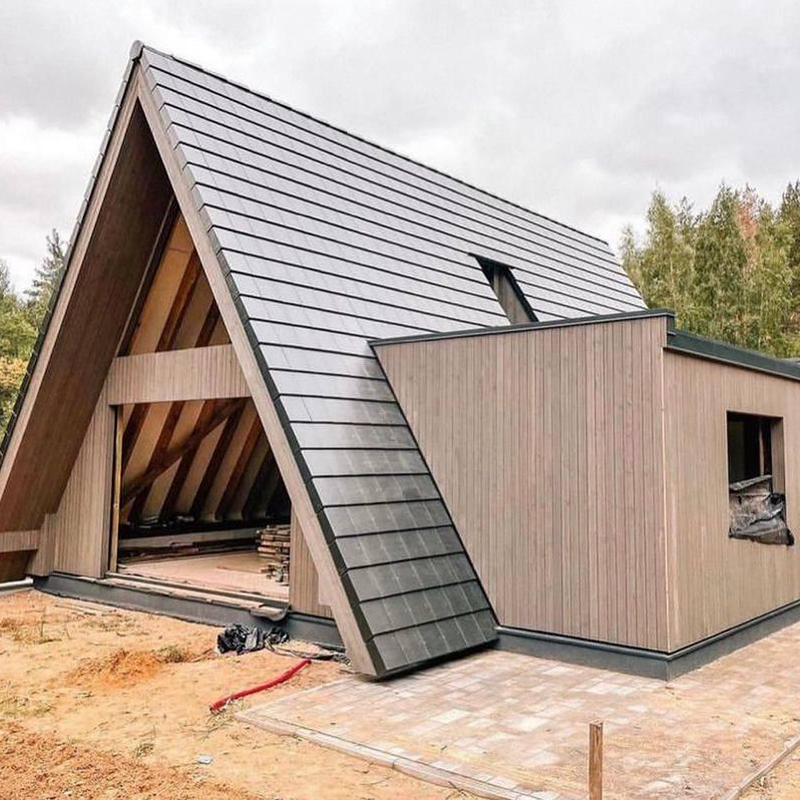

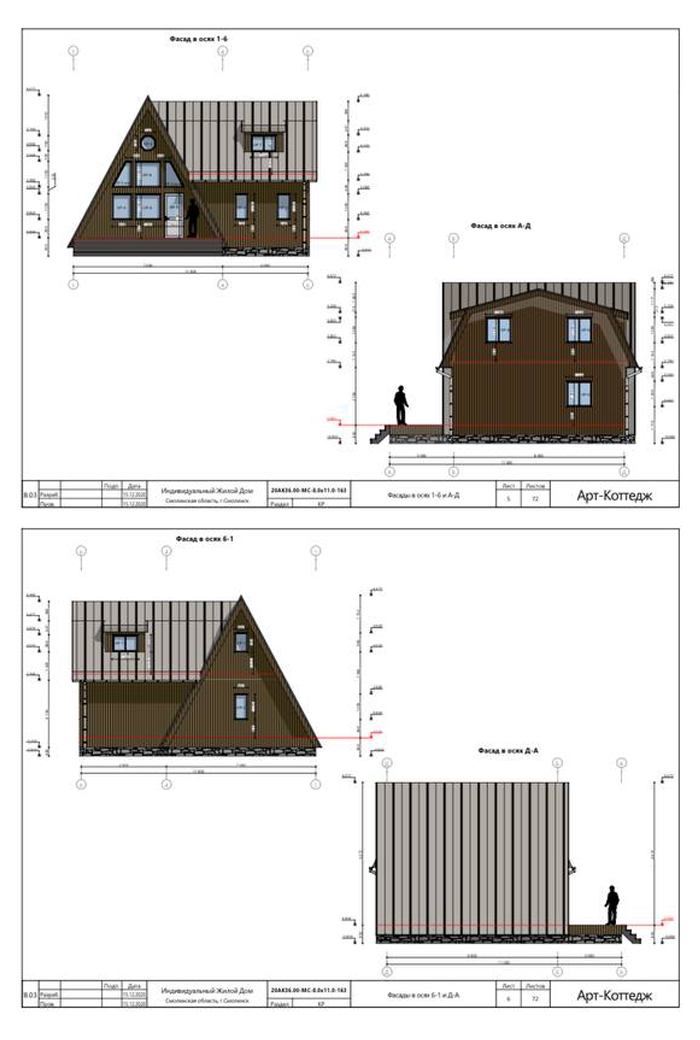
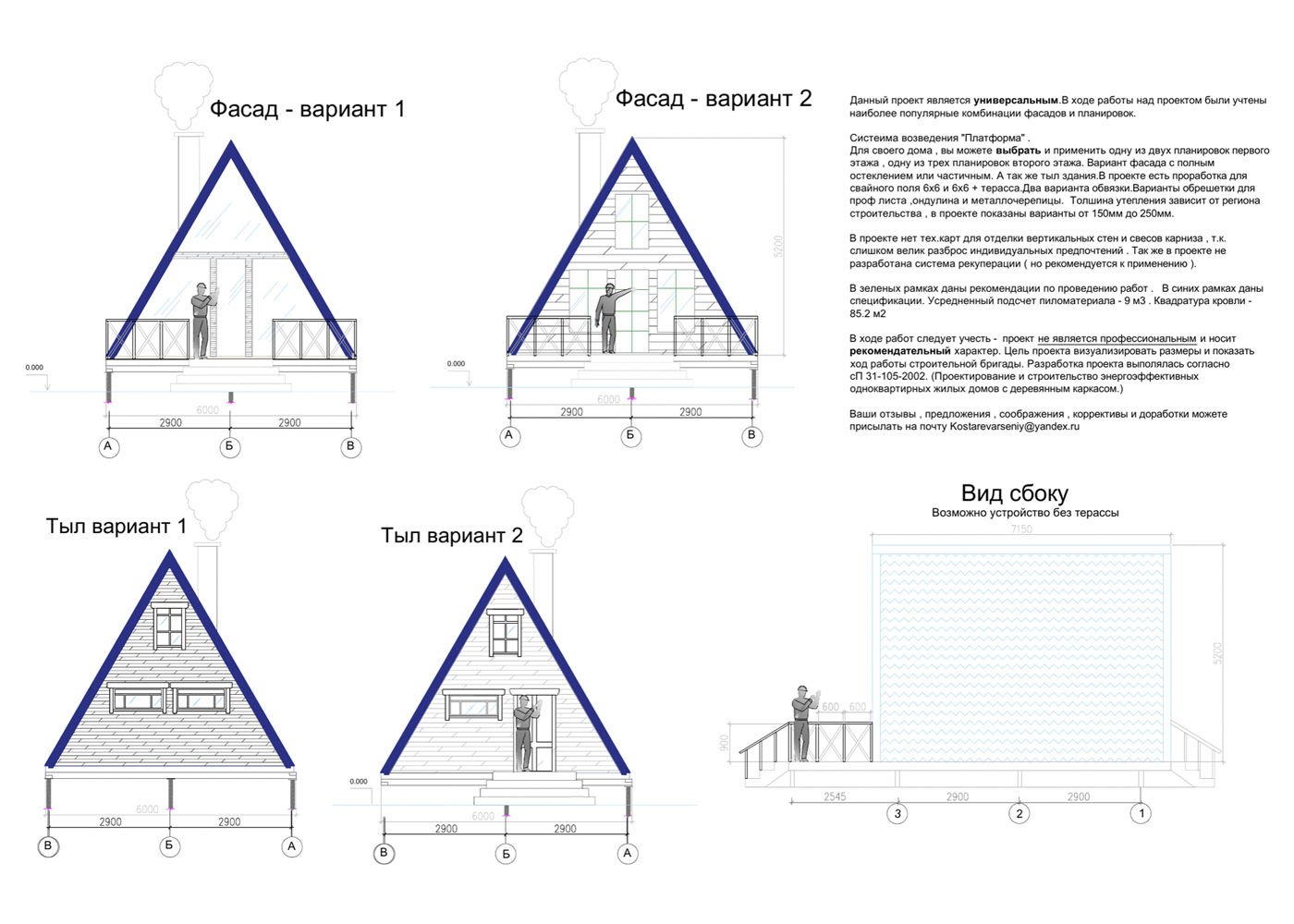
A-house projects
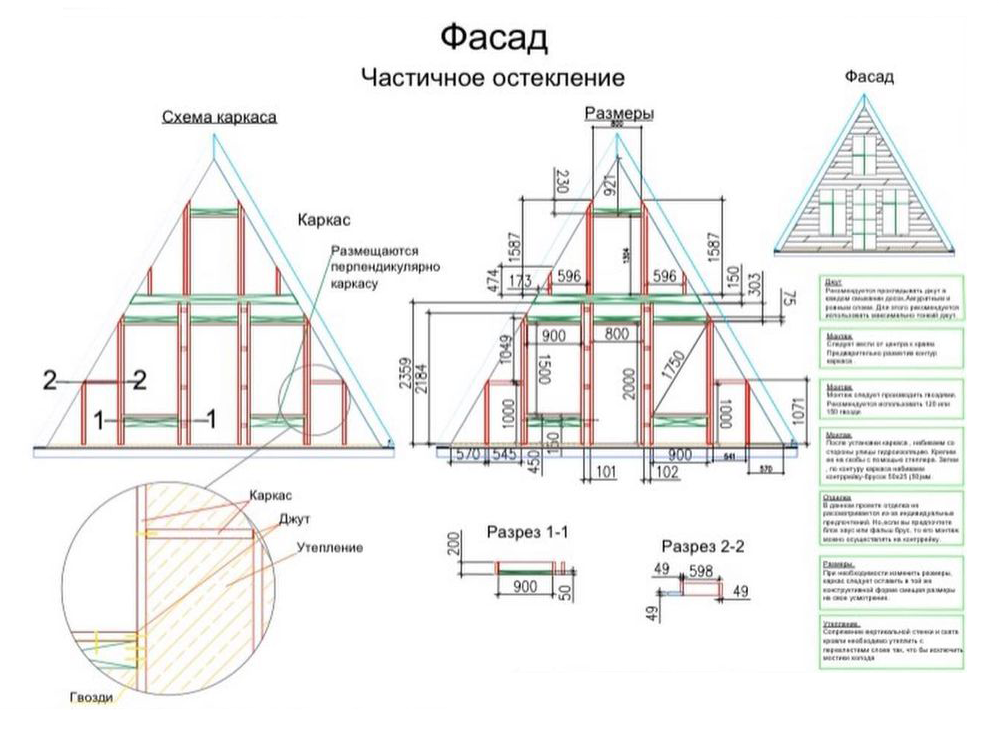
A typical design for an average triangular house has about 50 sheets and contains a description of key components, layout options and facade organization.
Here are some excerpts from my projects - they can give you a general idea of how an A-house is built .

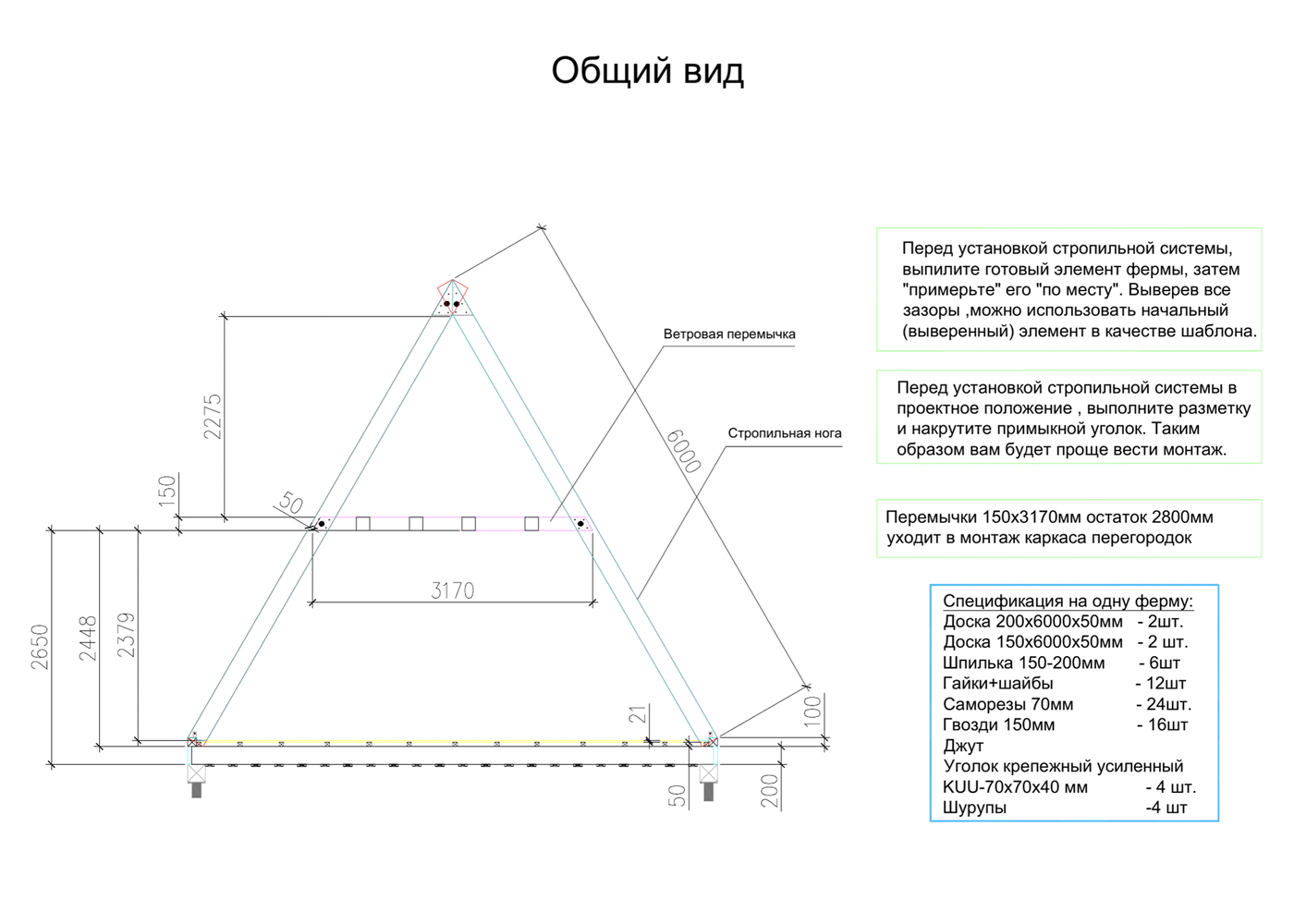
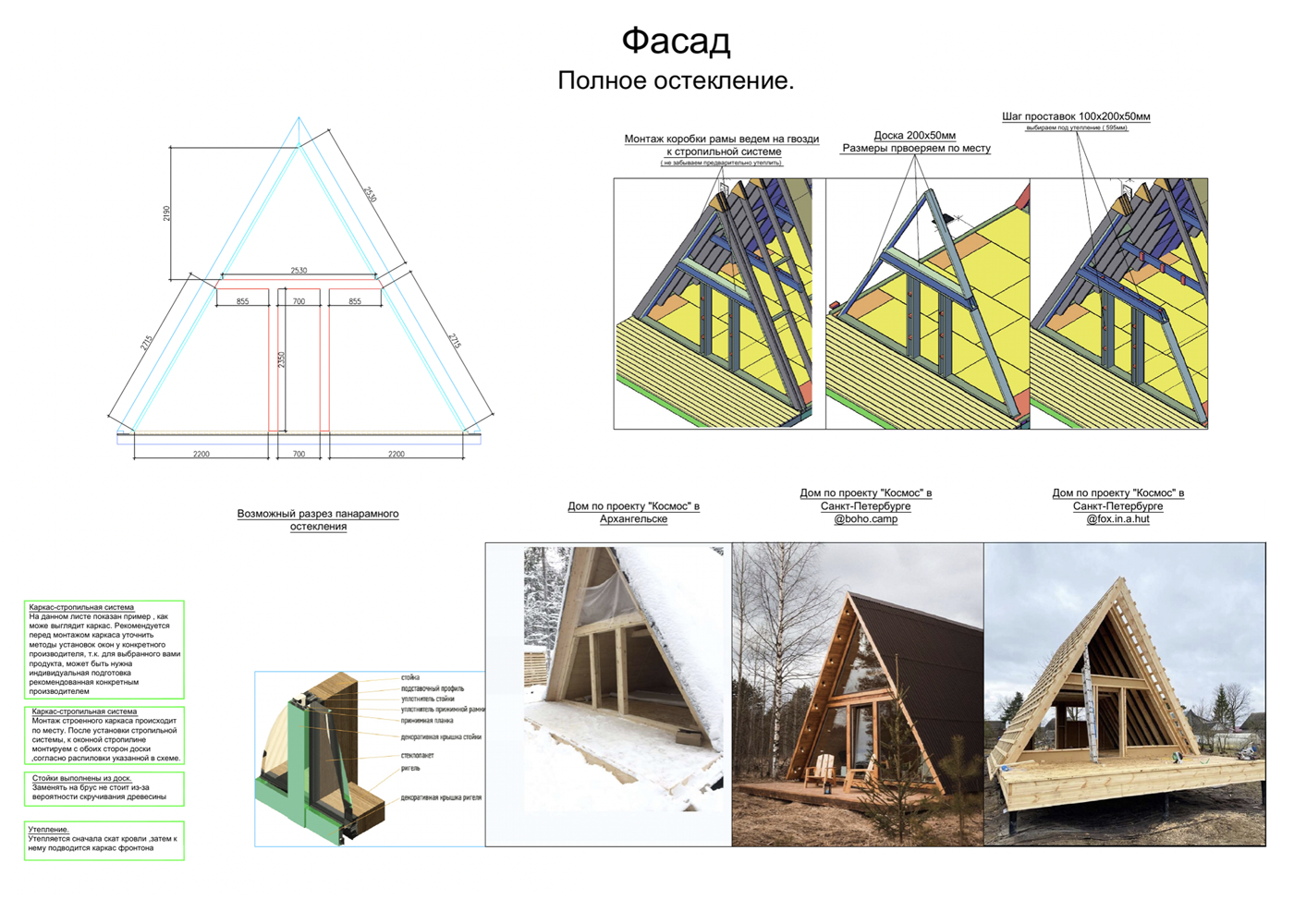
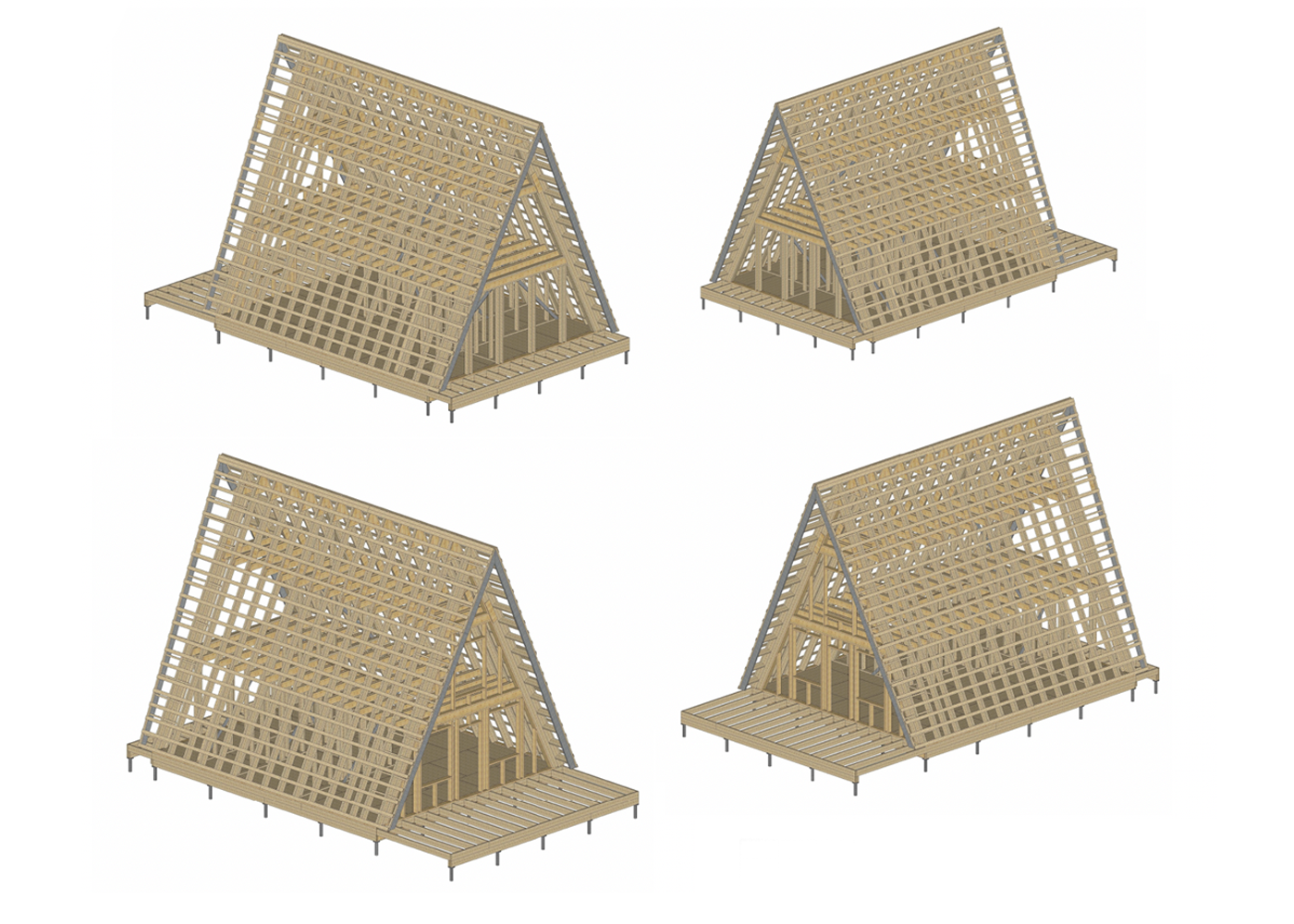
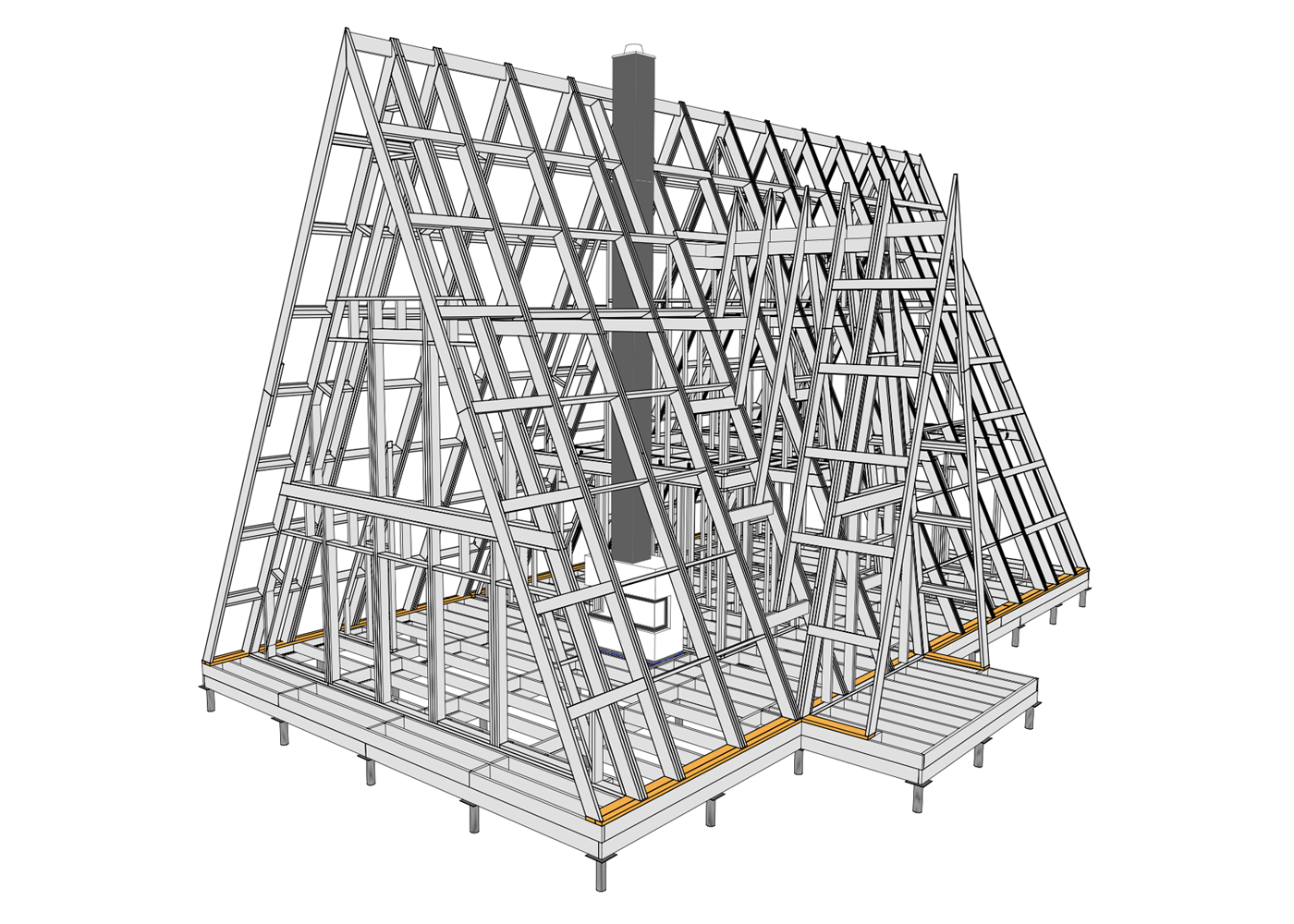
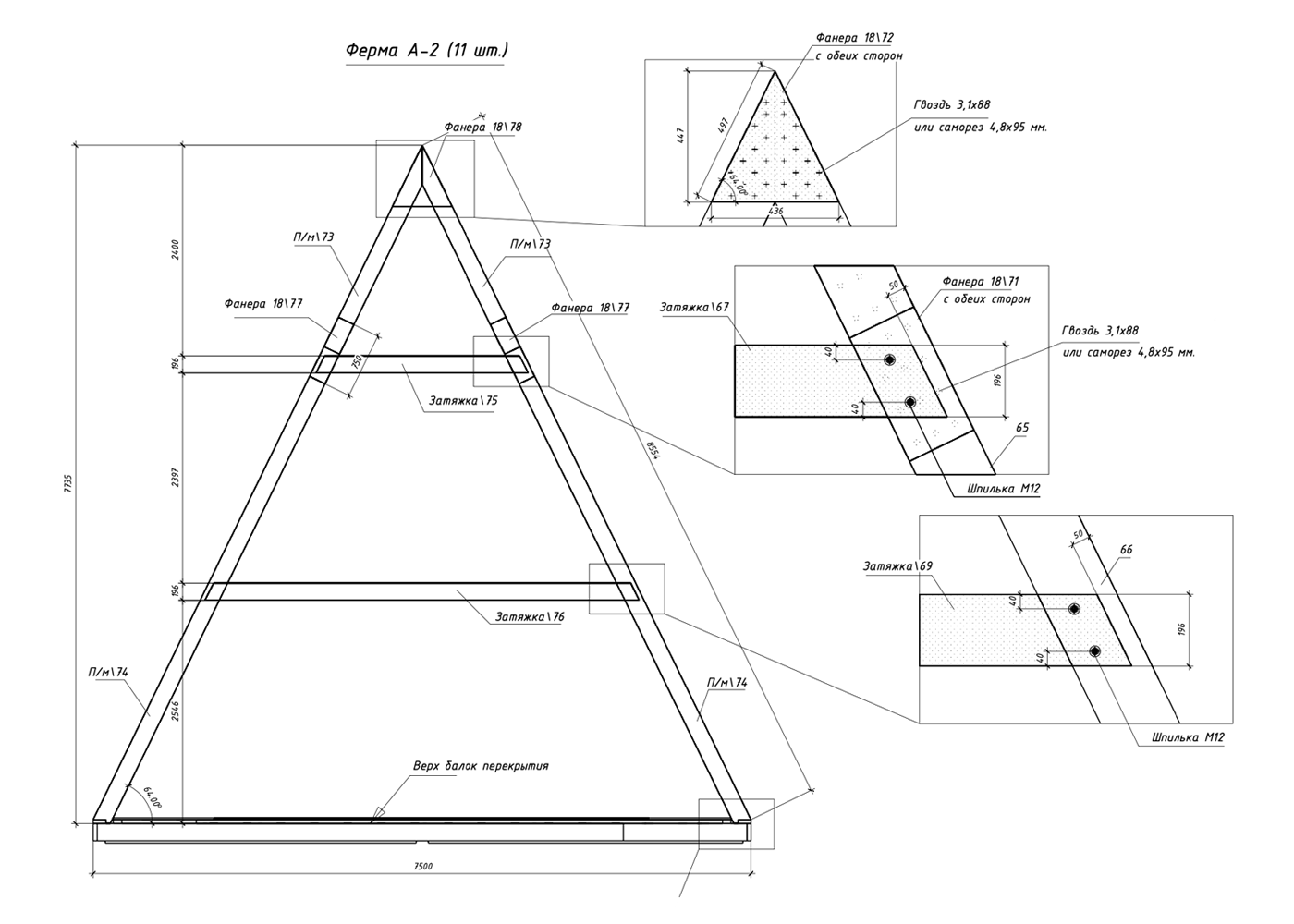
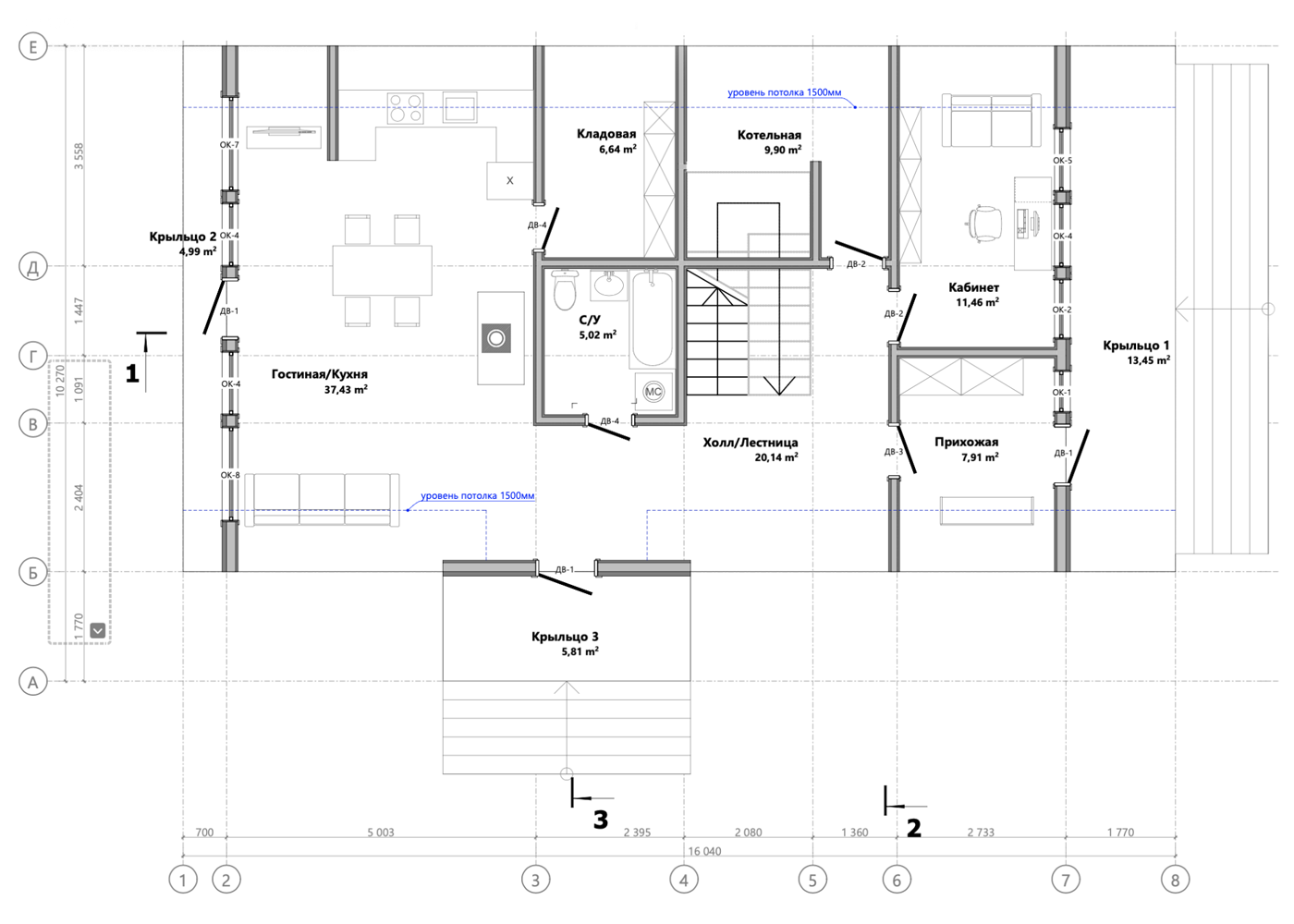
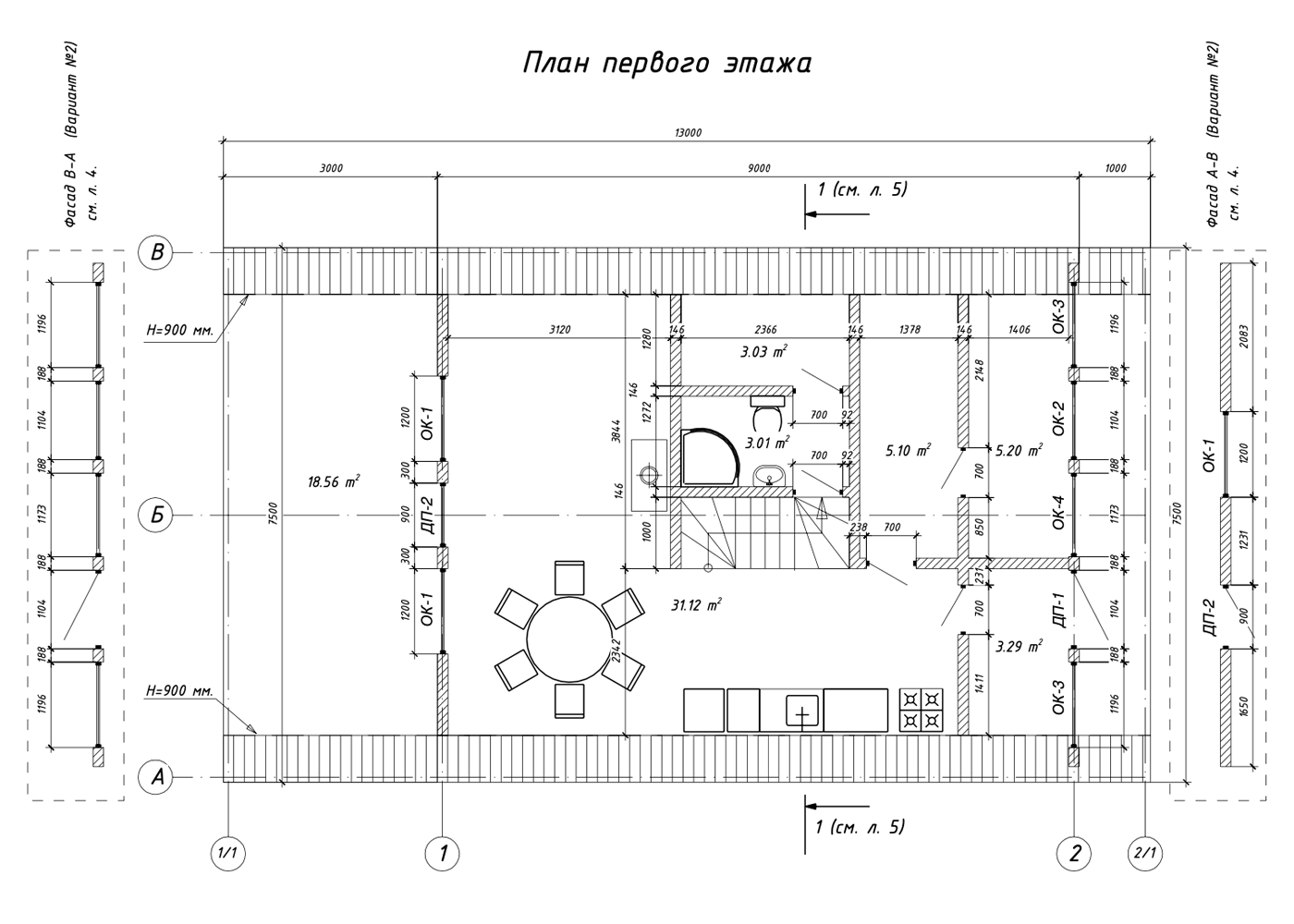
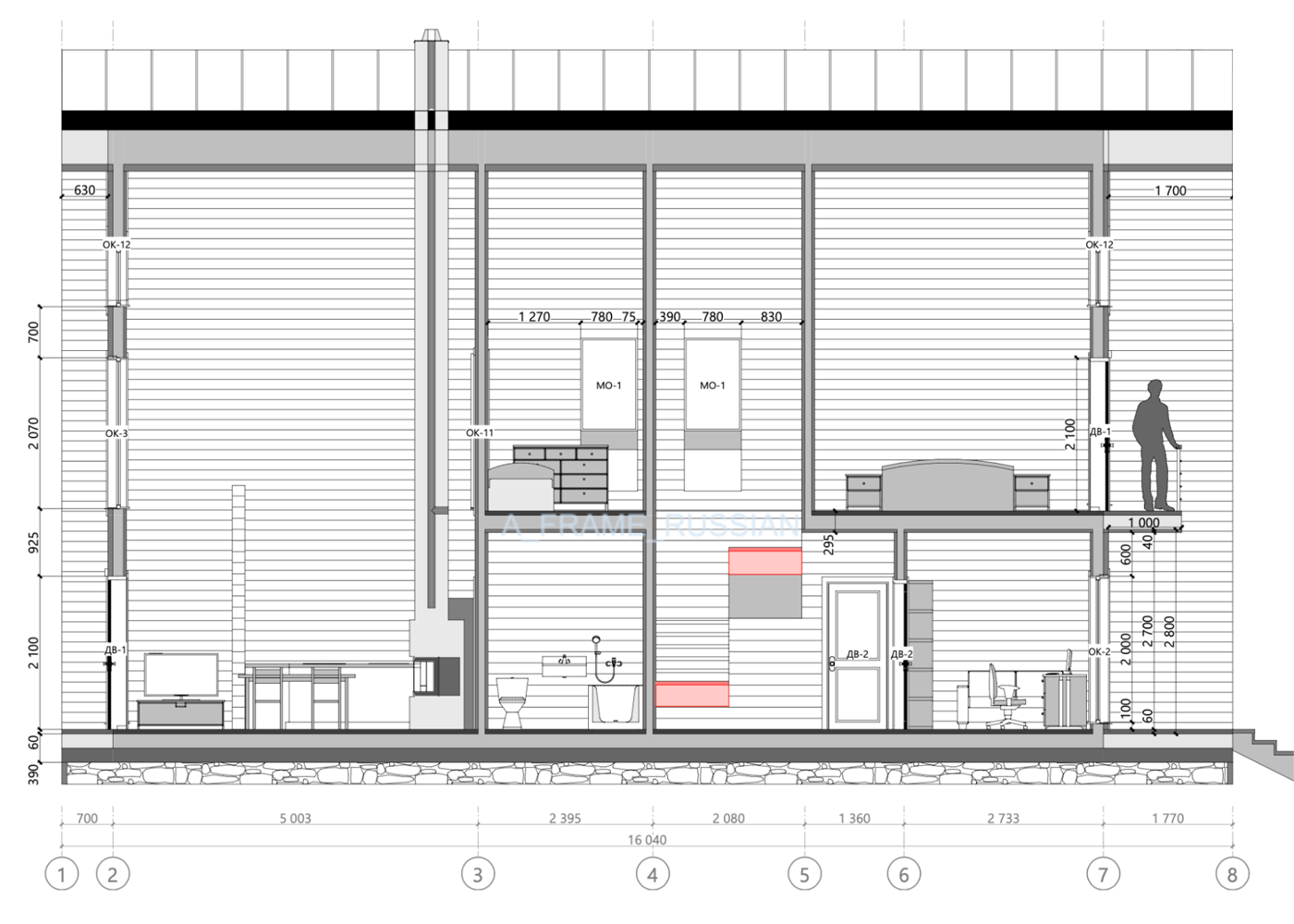
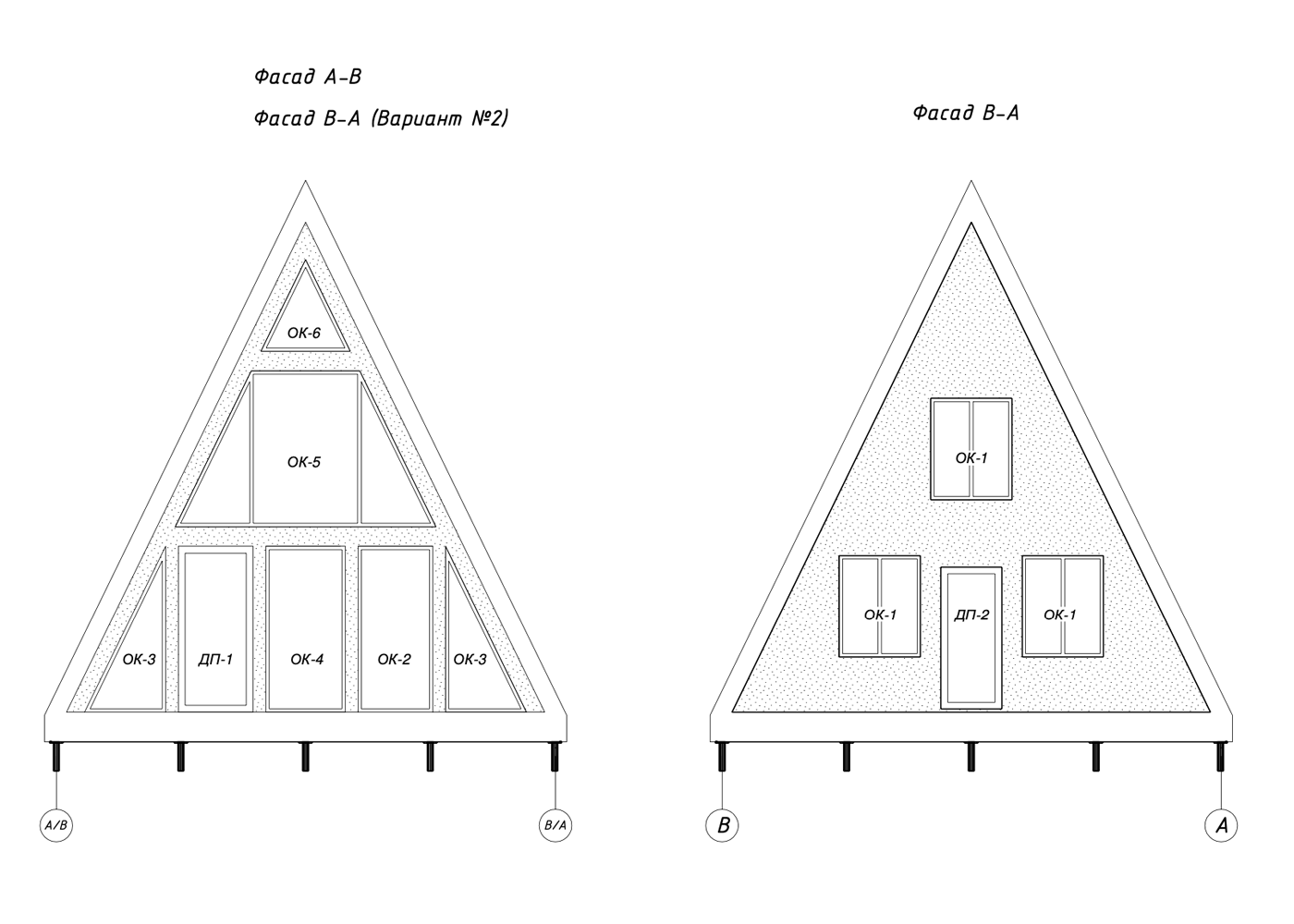
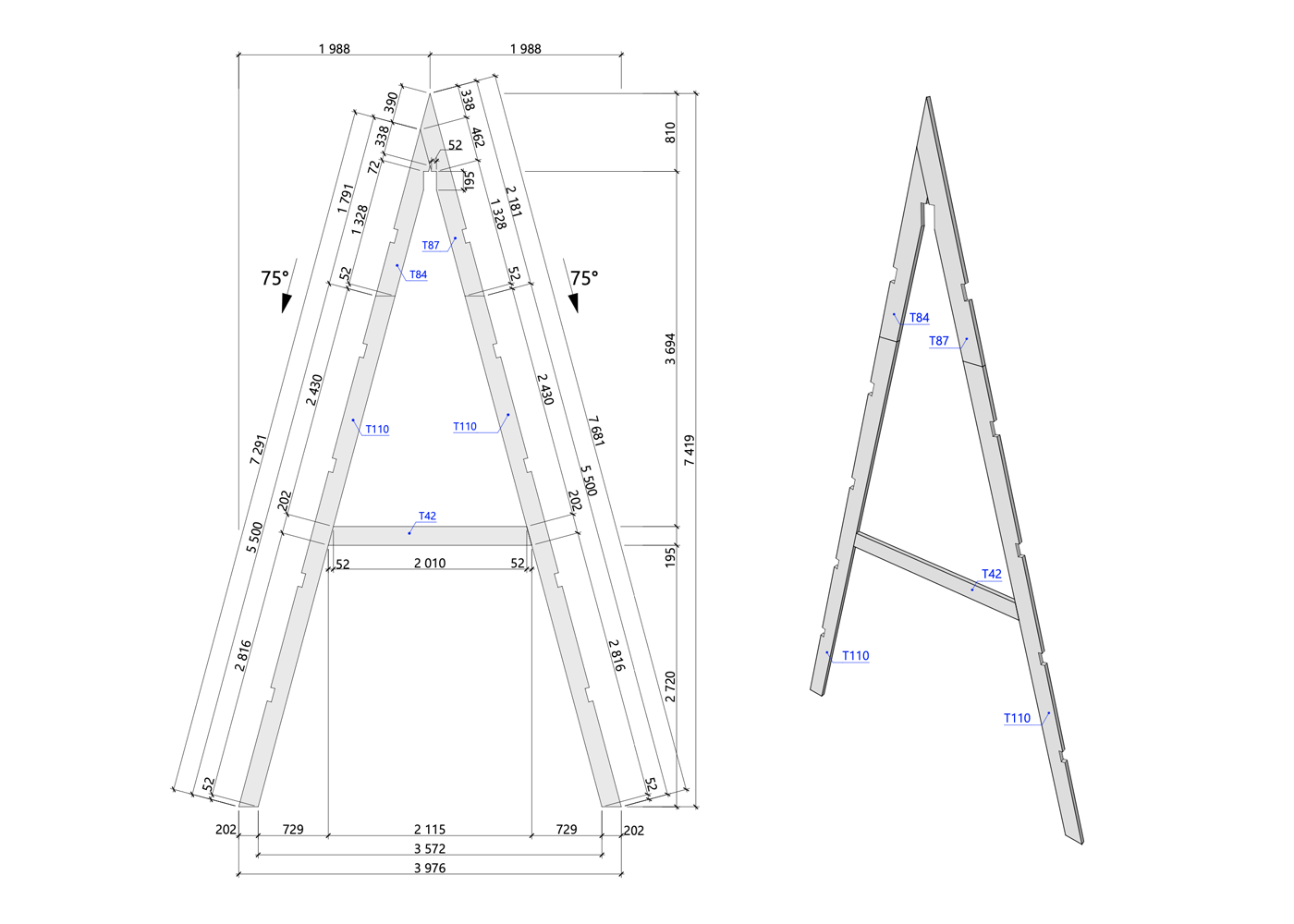
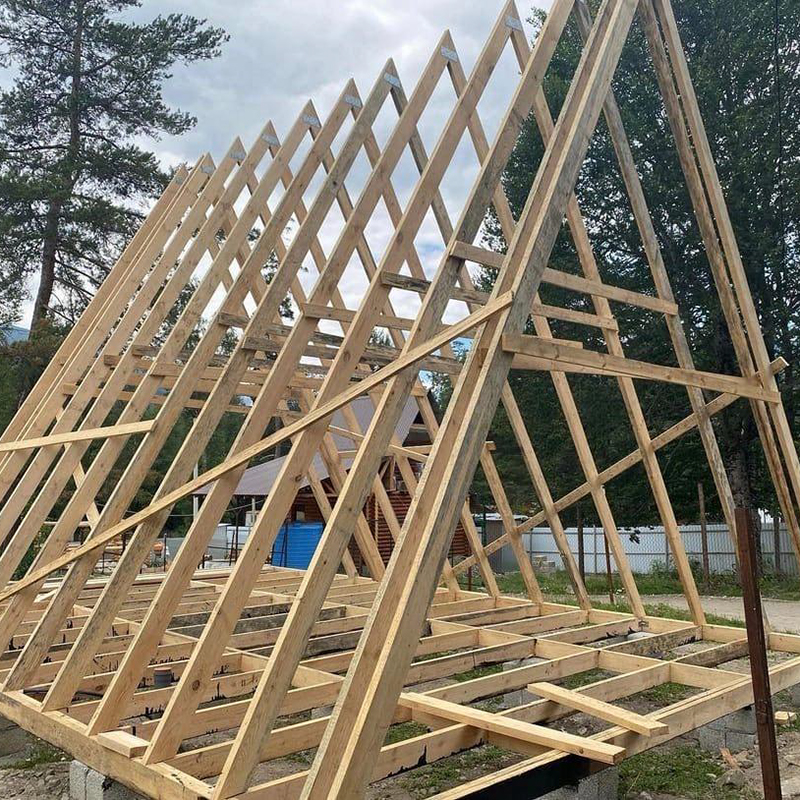
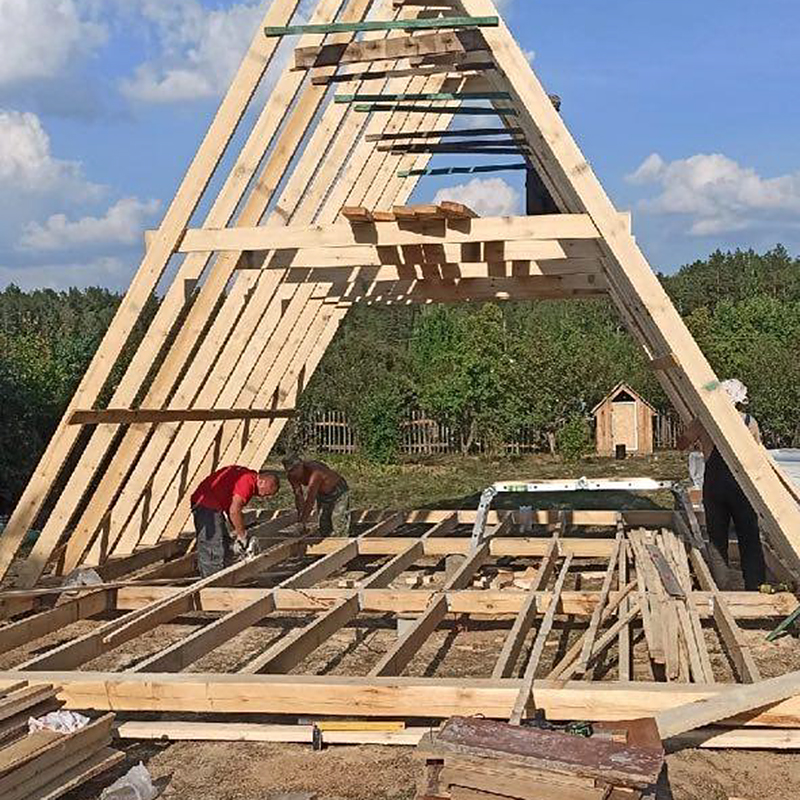
Features of A-frame construction
A-house is a regular house of non-standard architecture. That is, its vertical parts can be built, like any house, using any technology: frame made of wood or metal, concrete and brick. But the simplest and most popular method is a frame structure made of wood. Such a house is light and well insulated, it is easy to erect.
Here are some features that need to be taken into account during construction.
Orientation on the site. Because of the panoramic glazing, it may seem that it is better to orient the house to the south, and then it will always be light and warm. In fact, it is not recommended to orient it to the south, since all the interior decoration will fade and deteriorate under the sun's rays. This is the same as leaving furniture outside.
I recommend that owners orient the house with a glazed pediment to the west, this will save the interior and furniture. And also, when the sun sets, its last rays will warm the house a little. Maybe it is only 2-3 °C , but still not bad from the point of view of savings and comfort, if you live there permanently.
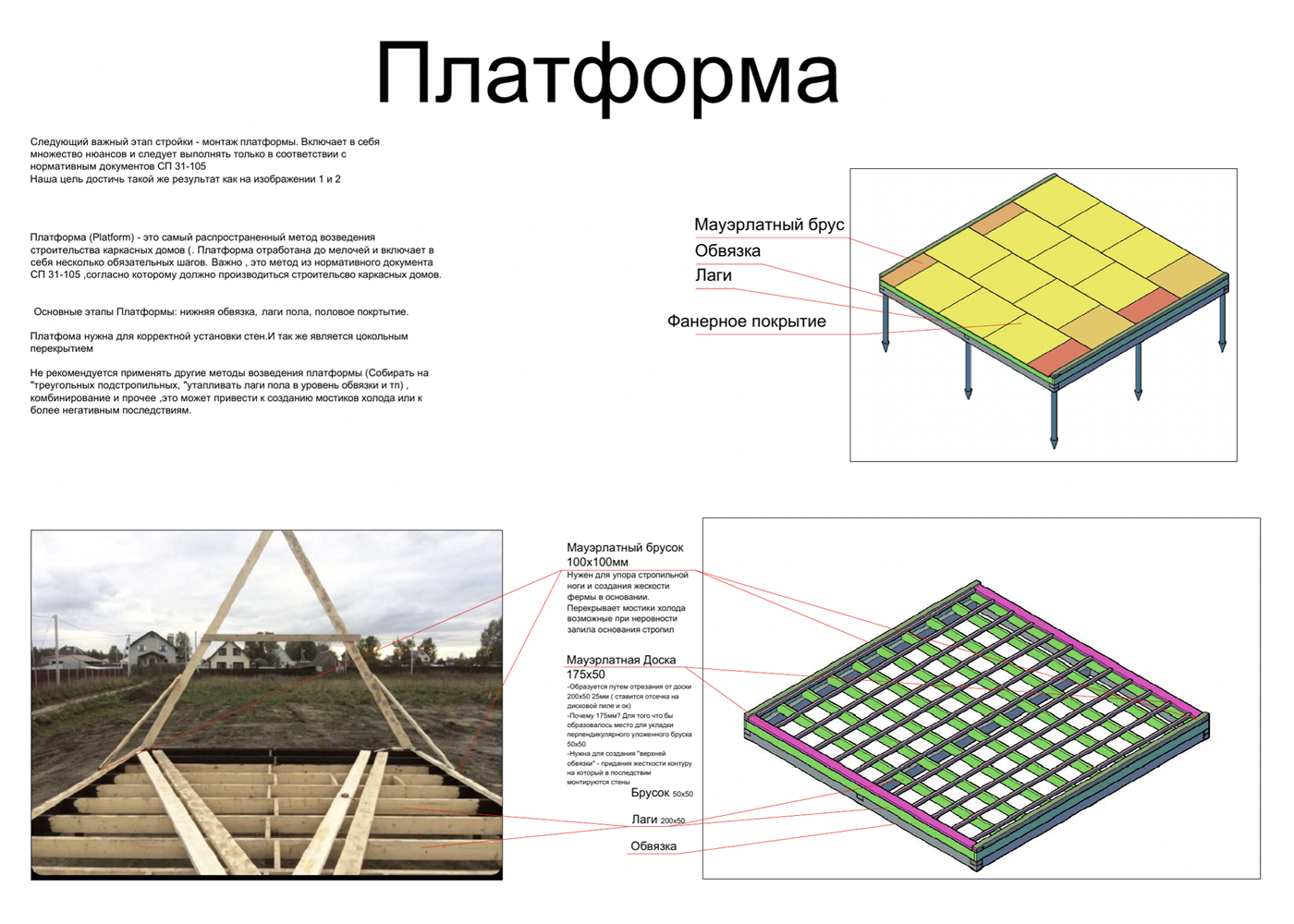
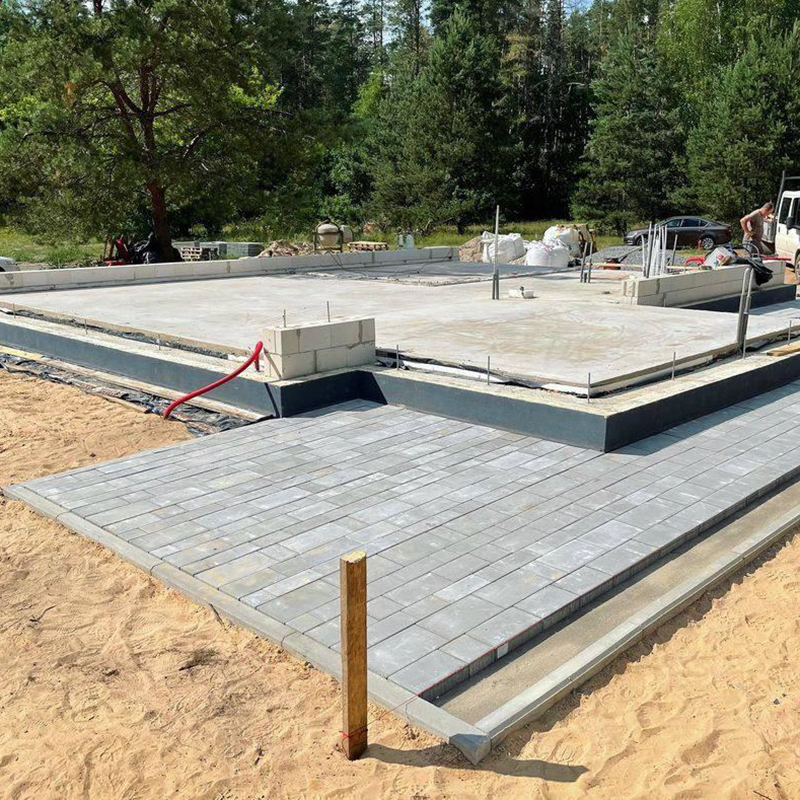
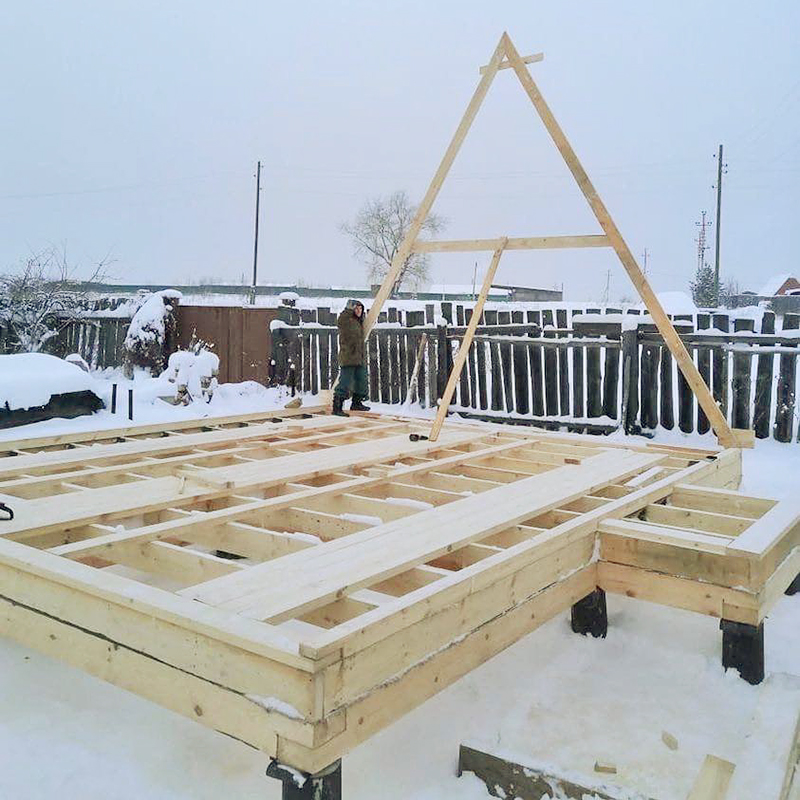
Foundation. Most often, screw piles are used as the foundation of a house - these are metal pins that are screwed into the ground like a screw.
A 6 x 6 meter frame house weighs 15 tons, theoretically it can be placed even on four piles, but, as a rule, a foundation with a reserve is made for such a house - from 9 to 15 piles. But even in this case, we get the most budget-friendly foundation option: 4,000 ₽ per pile including installation, that is, a maximum of 60,000 ₽. Several more piles are needed for the terrace, depending on its area.
A pile foundation is an optimal solution even on a sloping site, since the length of the piles can level out the difference in height. This often becomes one of the features of an A-house - it looks very cool on a relief site. Such houses are even built on the edge of ravines.
But the pile foundation also has its disadvantages, in particular a cold underground and a floor on wooden joists, which is more mobile than a monolithic one. Therefore, a concrete foundation can be poured under the A-frame - strip or slab.
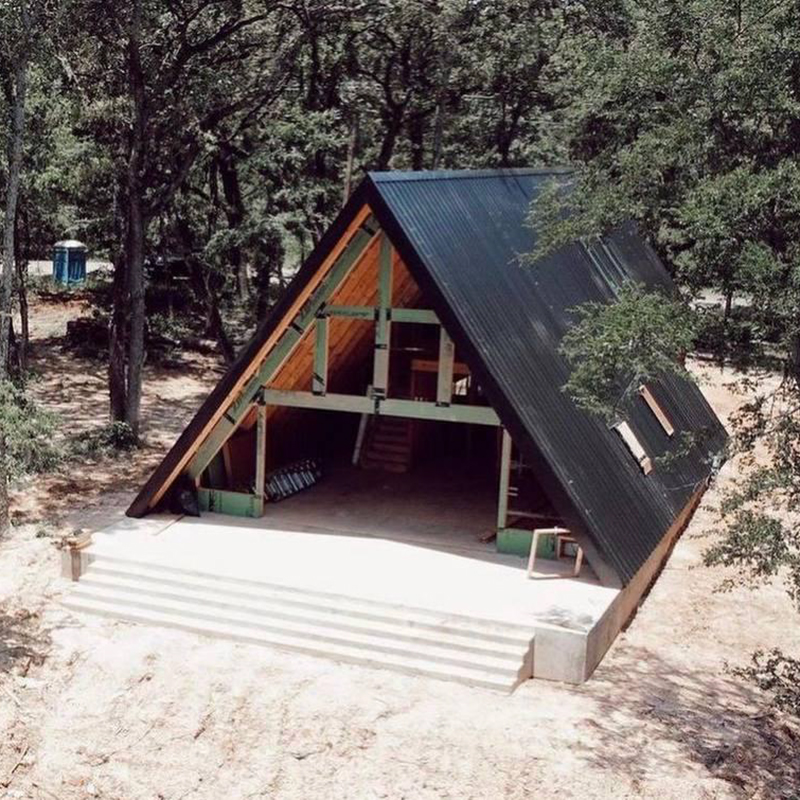
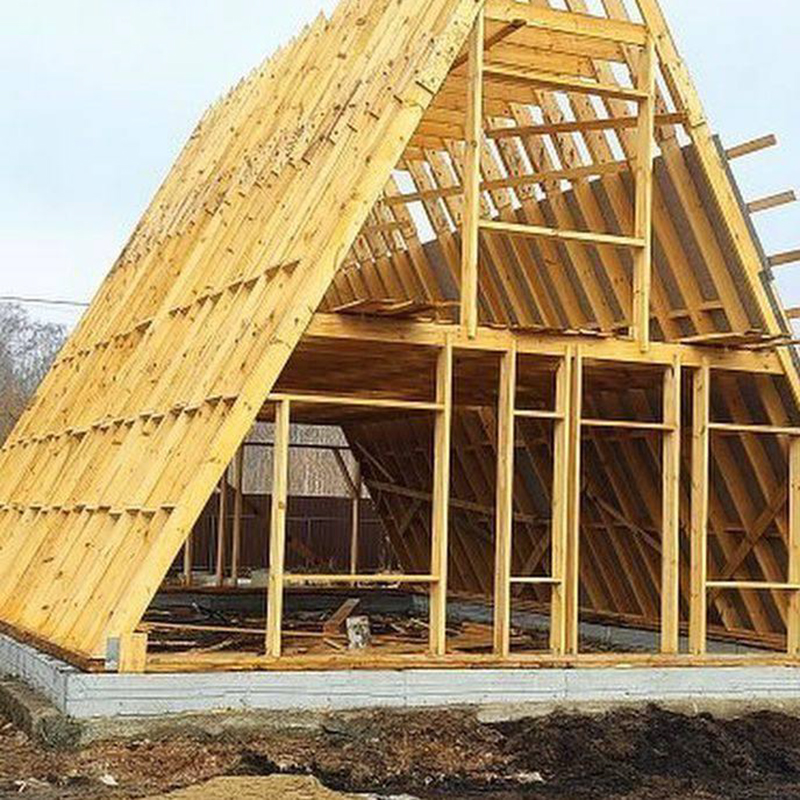



Pediments. The classic design involves panoramic glazing on the front pediment and one or two windows on the back side.
Windows are an important part of the cost of a house. For example, for a 6 x 6 meter A-frame with 6 meter rafters, windows will cost 100,000-300,000 ₽ , and for a 7 x 9 meter house with 8 meter rafters, the price of windows will be at least 400,000 ₽. These are all windows, including those on the back side.
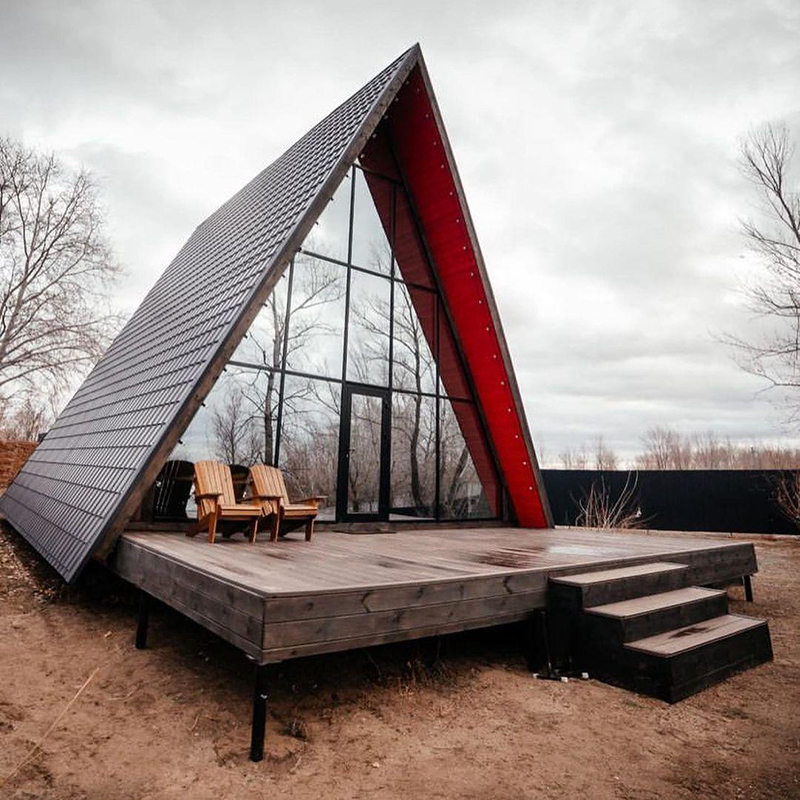
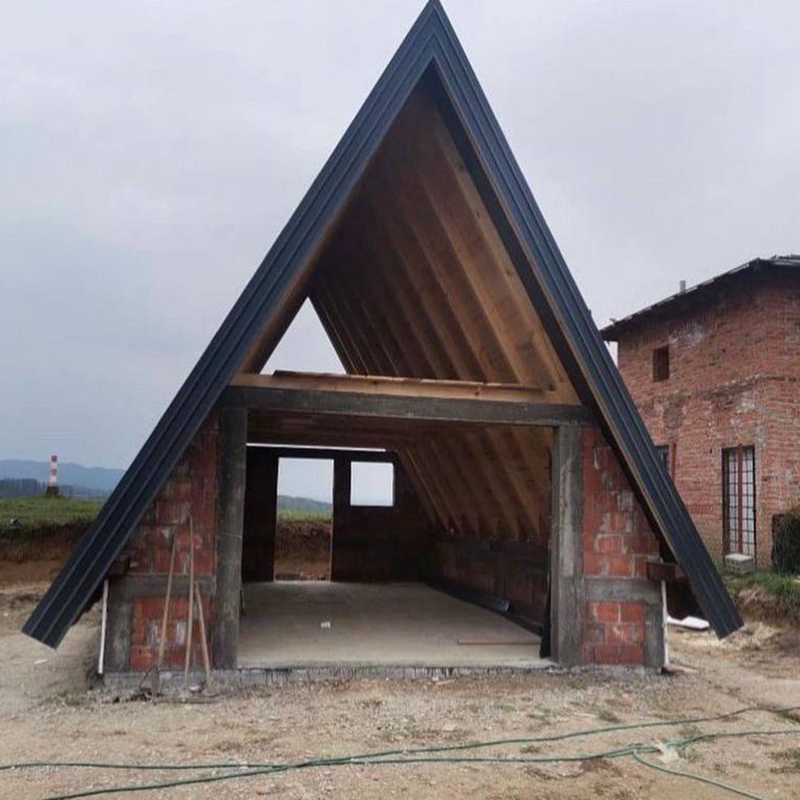



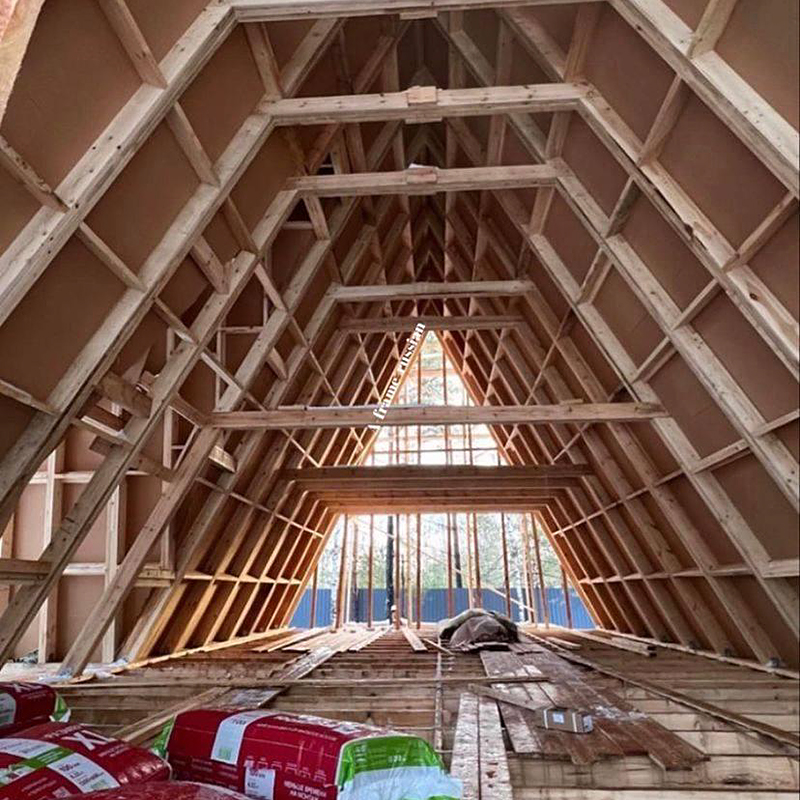
Roof. Usually, A-houses are built using frame technology. The usual roofing rules apply here: insulation is laid between the rafters, battens and counterbattens are made for the roofing material, and vapor barrier and moisture-windproof films are stretched.
Regular metal tiles are suitable as a roofing material. They are not as noisy in the rain as it may seem. If there is 200 mm of thermal insulation, then raindrops practically do not interfere. You can use soft roofing technology, when the rain is not heard at all, but this is twice as expensive.
For example, 1 m² of metal corrugated sheet in 2024 costs about 800 ₽. Flexible tiles — 600 ₽ per 1 m², but you also need a special lining carpet under it, this is an additional 245 ₽, and OSB boards — 500 ₽ per m². In total, it comes out to 1345 ₽ per 1 m². For an A-house 6 × 6 meters with 6-meter rafters, the roofing area will be 100 m². That is 80,000 ₽ if you buy corrugated sheet, and 134,500 ₽ if you buy flexible tiles. These are the prices for materials only, without installation.
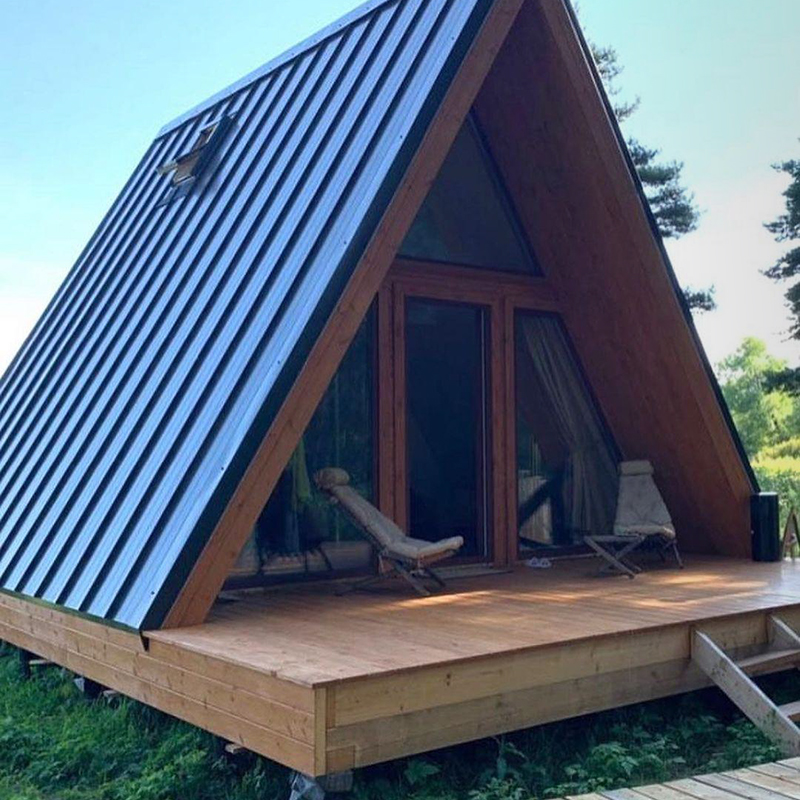
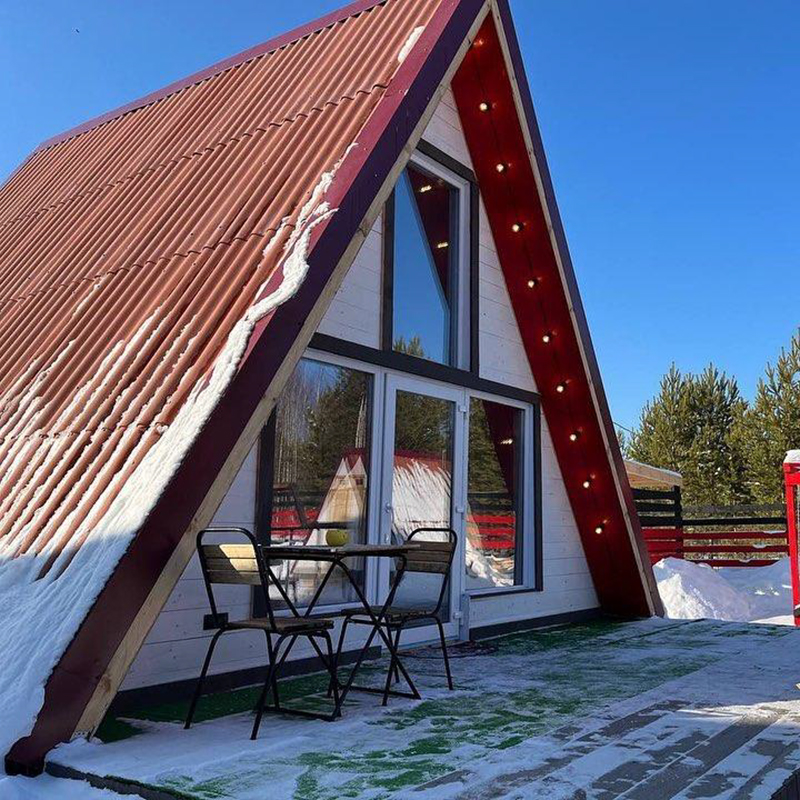
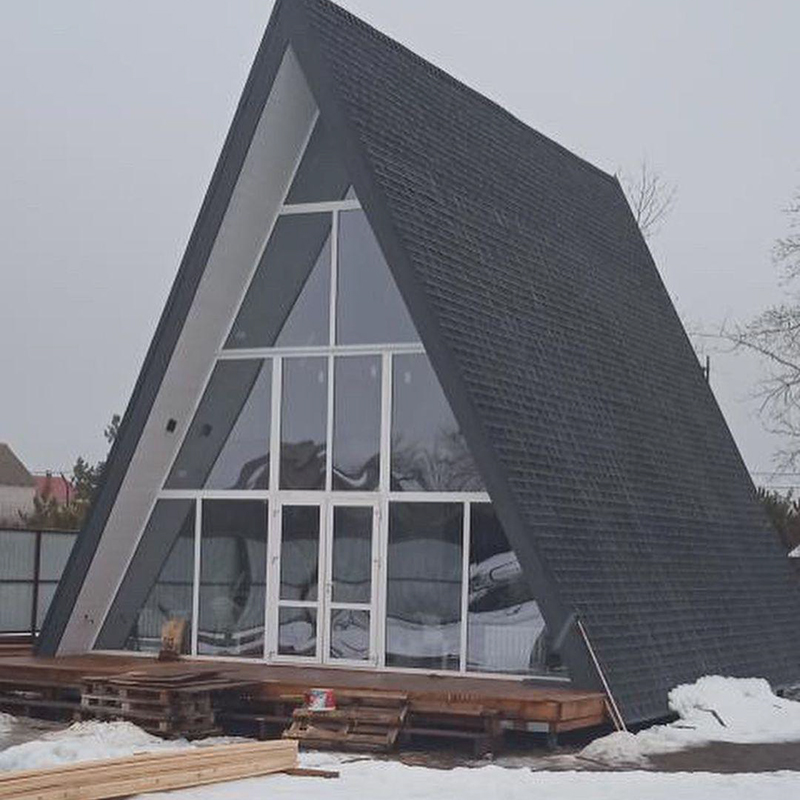



Mistakes in building hut houses
When it comes to building an A-frame, a lot depends on the team. I have repeatedly spoken with customers who were forced to change builders or received a project with problems. And the peculiarity of private housing construction is that many problems begin to emerge after several years of using the house, when there is no one to make claims to.
I do not recommend working with builders who boast of their experience and say that A-house is not a house at all, and building it is a piece of cake. I started as a roofer myself and I know that you can make many mistakes. They are mainly related to the roof structure. Here are some of them:
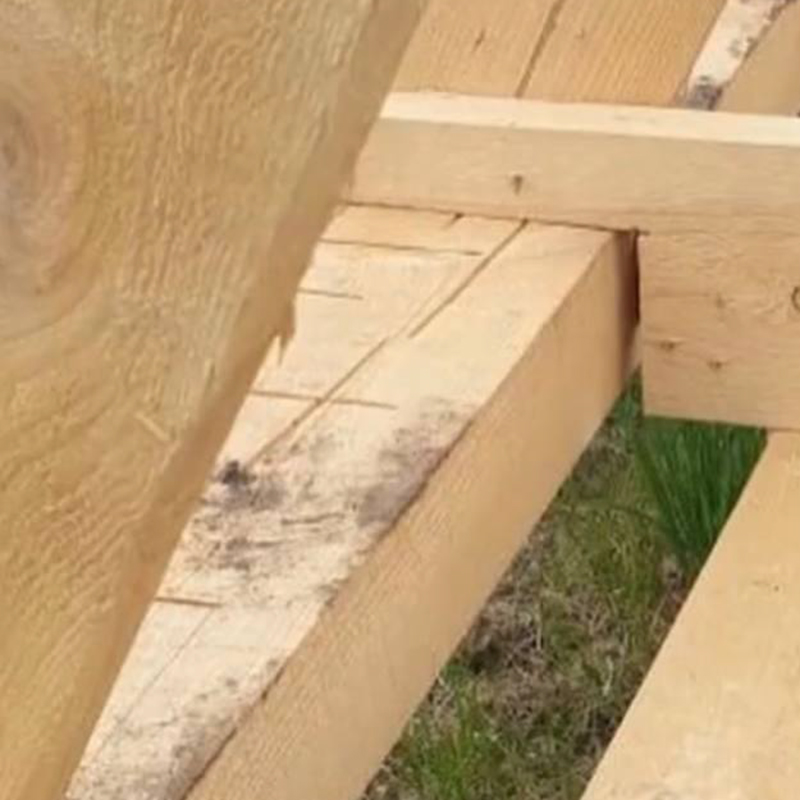
- Incorrect rafter extension. With a standard board length of 6 meters, as it comes from a sawmill, you can only build a small house, usually 6 × 6 × 6 m. To increase the height, the rafters must be extended. For this, only kiln-dried boards are used: if you nail a board of natural moisture with nails, it will shrink, and a through gap will appear between the boards.
- Poor waterproofing of the place where ventilation pipes and chimneys pass through the roof. During rain, a leak starts around the pipe, moisture gets into the insulation, and then simply drips from the ceiling. You have to climb in and redo it. These mistakes are especially common if the roof angle is more than 65°. For such a roof, even finding a ventilation pipe is a separate problem.
- Metal roofing tiles can stretch if handled carelessly. As a result, the roof will be unsightly - with an uneven pattern or seams that bulge.
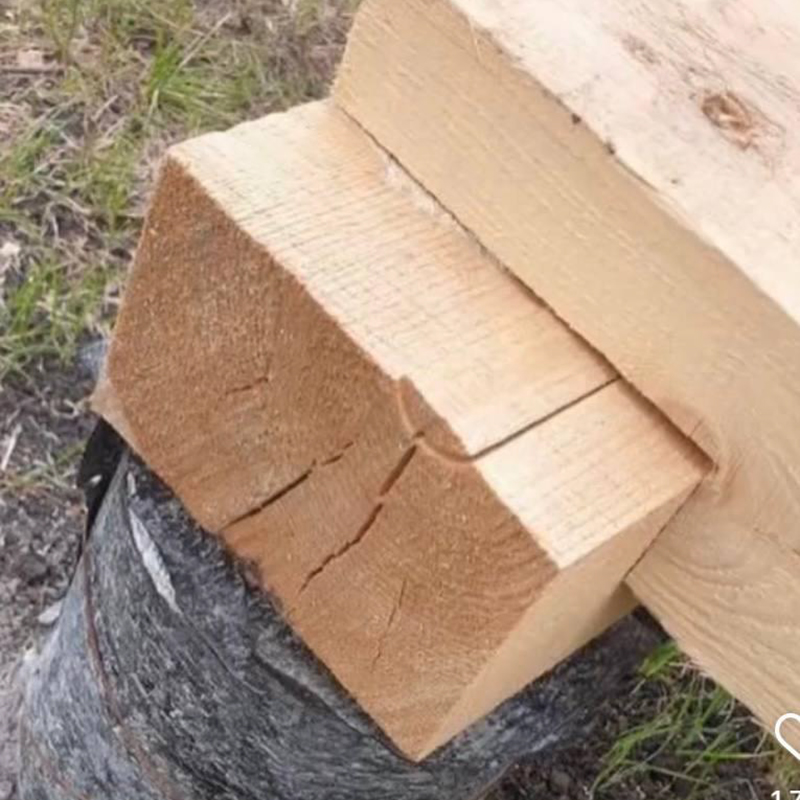
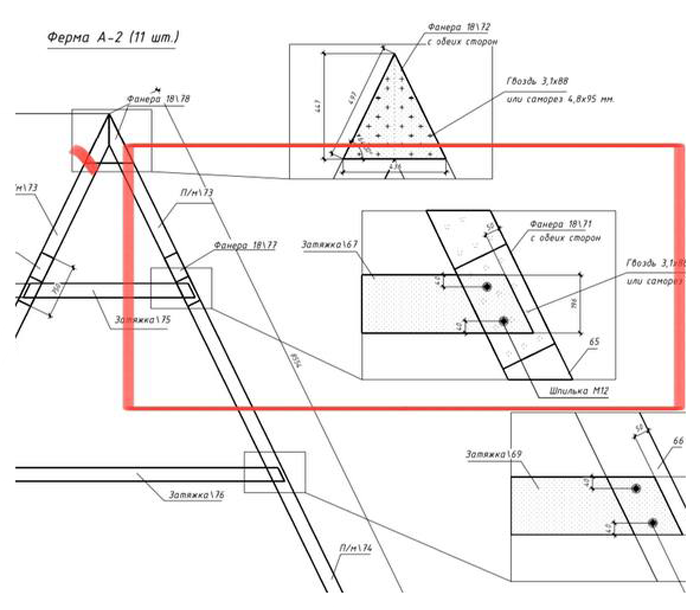

There are also general construction errors - they forgot to install a vapor barrier, fixed it on the wrong side, or installed the lathing incorrectly. I saw a house where the builders mixed up the vapor barrier and the moisture and wind protection, and the team convinced another customer that the vapor barrier was not needed at all, since the house "must breathe."
Another very common problem is with the installation of joists and the floor. To avoid gaps and drafts, a kind of platform is built on the strapping beam, inside which the joists are. Then the floor is laid on top. With this technology, the elements can shrink or move slightly between themselves, but this will not affect the thermal insulation of the house in any way - there are no gaps.




How much does it cost to build an A-frame
People often think that an A-frame is cheaper than a house of standard geometry. This is not true. An A-house can cost a maximum of 10-15% less, and often the same. For example, a small A-frame of 6 x 6 meters in 2024 will cost from 1.5 to 2.5 million, depending on the materials and interior.
Let me explain what the cost is made up of. You can use a board with natural moisture from a sawmill. For example, a board of 50 × 150 × 6000 mm in 2024 costs about 400 ₽. The same dry board of chamber drying - 1125 ₽.
The second option is, of course, better, because the board with natural moisture starts to dry after installation, which leads to the appearance of cracks and cold bridges. As a result, the house is cold, and the owner curses the frame technology, the builders and the tent-houses . Although it was simply not necessary to save on wood.
You can heat a house with two convectors for 10,000 ₽, or you can install a warm floor system and install a boiler. This is no less than 100,000 ₽, depending on the complexity of the system.
Therefore, if builders offer to build an A-frame much cheaper than a regular house of similar area, I would not deal with them. More than once I have seen how seemingly experienced builders said that they would make an A-house for half the price - after all, there is only a roof. They started doing it, and it did not work. In addition, there are a number of features that not everyone will understand: for example, joining long rafters when working at height.




How much does it cost to operate an A-frame?
There are no statistics in Russia on how many A-houses have been built , but it seems to me that there are no more than a thousand of them in the entire country. I mean real residential buildings, not summer cottages from the eighties and nineties that stand in SNTs and have already been abandoned. We do not have much experience in operating huts . I suppose there are only about fifty examples that are more than ten years old.
However, American houses stand for over half a century, although the technology and materials in the fifties and sixties were at a lower level than now. In general, frame technology suggests that a house can stand for a hundred years if the construction technology is followed and moisture does not get on the boards.
As for the operating costs, I visited the owners of A-frame houses in winter and specifically asked about their bills. Overall, there is nothing unusual here: the energy efficiency of an A-frame is the same as that of a regular frame house. In a 90 m² house heated by an electric boiler, the owner will pay 5,000-6,000 ₽ for electricity, including all other needs - kettles, a boiler, an electric stove and lighting.
I am not a lawyer and rely only on the experience of my clients, who have not yet had any problems with registering A-frames . This is an ordinary house on a foundation. If it has two floors, then legally it is also two floors, in documents from Rosreestr it will be designated as a two-story house.
The only exception is if the house is not on a solid foundation. For example, if the A-frame is simply placed on bricks. Then it is no longer a solid structure, so it will not be possible to register it as a house.
Also, the procedure for registering a house depends on the land category: individual housing construction, private household plots, gardening non-profit partnerships, etc. If this is an agricultural plot, then it will not be possible to register a residential building on it.
I think there's a lot more flexibility with A-frames than with regular ones. For example, one of my clients registered an A-frame on a lake as a boat garage. The house is right on the water, and the owner lives there periodically.
Triangular houses have both advantages and disadvantages:
- Special architecture - such a house will stand out in any average low-rise village.
- A-house is easy to maintain. Since there are no facades in the usual sense, there is no need to paint, repaint or plaster them. Panoramic glazing only needs to be washed occasionally, and metal tiles do not require any maintenance.
- There are no load-bearing walls inside, as the roof is assembled using trusses - cross beams that help distribute the load. Due to the triangular shape, there is no need to transfer this load from the roof through the walls to the foundation. Therefore, the A-house is convenient for redevelopment; any configuration of rooms can be quickly created inside the living space.
- A triangular house is stronger than a house of classical shape, because a triangle is the strongest shape in geometry. For example, you don’t even have to calculate the snow load on the rafter system, because the roof angle is so steep that snow does not stay on it.
- The A-frame has less usable volume than a classic house. Dead zones in the corners can be used as storage space, but this is obviously uninhabitable space.
- A triangular house needs to be carefully thought out from the inside in advance. It is already difficult to seriously change something in the layout after construction. And if there is not enough space, you will either have to put up with it or make an extension that will distort the appearance of the A-house .
Briefly about A-houses
- When designing an A-frame, it is worth paying special attention to the location of the stairs - it is better to make a larger house, but with a convenient staircase. Do not cut the space in favor of the living room, forgetting about how to get to the second floor.
- An A-house is a regular house of a non-standard shape, and it is wrong to think that it will be much cheaper than classic houses. In addition, in terms of square meters, it can be more expensive, because with the same foundation, A-frames have less living space.
- An A-frame house is easier to maintain than a regular one, but it is more difficult to build. The higher the A-frame , the more complex it is: for example, you need to extend the rafters. It is better to invite builders with experience in building triangular houses to do this kind of work.
- In a triangular house, you can install all the same communications as in a regular one. The boiler is placed in a special technical room, or you can do without it and heat the house with convectors.
- The best technology for building a tent house is frame construction. This makes the house warm and light, and it can be placed on a foundation made of metal piles, which will be cheaper.
Post a Comment